Difference between revisions of "Ineos"
(→Meetings on shale gas with UK government ministers and officials) |
m (category consolidation - changed 'Chemical industry' to 'Chemical Industry') |
||
| (207 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ''' | + | {{Template:Fracking badge}}'''Ineos''' is a major chemicals company and a 50 per cent owner of the Grangemouth refinery in Scotland. It is part of the Ineos Group, a privately owned multinational chemicals company partly-headquartered in Rolle, Switzerland, with its registered office in Lyndhurst, United Kingdom. |
| − | + | British billionaire Sir [[Jim Ratcliffe]] is the founder, chairman and main shareholder, owning 60 per cent of the business. In 2018 he was ranked as Britain's wealthiest person in the annual ''Sunday Times'' Rich List after an extraordinary £15 billion rise in the value of Ineos from 2017. He was also knighted in the 2018 Queen's birthday honours list. | |
| − | In | + | Once described as 'the biggest company you've never heard of', Ineos has more than 80 separate firms registered at the UK Companies House. It is the largest privately owned company in the UK. <ref> Nick Mathiason, [http://www.theguardian.com/business/2010/mar/04/ineos-tax-breaks-plans-move Ineos tax deal sparks fury as firm plans move to Switzerland], theguardian.com, Thursday 4 March 2010 21.05 GMT </ref> In 2013 the Group's turnover was £43 billion; by 2017 this had risen to over £60 billion according to the ''Sunday Times'' Top Track 100. |
| + | |||
| + | Ineos has made major investments in shale gas exploration in the UK, buying up licences from [[BG Group]] and [[IGas Energy]] since 2014. It is the UK's largest shale explorer in terms of exploration licences held. In July 2016 Ineos announced it intended to accelerate UK shale gas development by lodging as many as 30 planning applications to drill test fracking wells in the north of England in early 2017. It said it hoped to begin extracting gas within 18 months. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Director [[Tom Crotty]] said he believed that once drilling started, people would 'see [fracking] is not the Frankenstein monster they thought it was'. According to the ''Financial Times'', 'he was confident that recent changes to rules allowing ministers to intervene if local councils delay granting permission would finally lead to Ineos drilling test wells'. Until permission was granted, he admitted it 'would continue to be “difficult” to convince critics'. <ref>Peggy Hollinger, Industry Editor [http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/32d8779a-4c36-11e6-88c5-db83e98a590a.html Ineos targets British test wells to kick-start shale gas market], ''Financial Times'', 17 July 2016, accessed same day </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In addition to its shale gas acquisitions, Ineos paid £1billion for the oil and gas business of Danish firm [[Dong Energy]] in May 2017, in a buying spree that also included £200m on a North Sea oil pipeline from [[BP,]] securing it a position as one of the top 10 biggest oil and gas producers in the region. | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
| + | INEOS Group is the fourth largest chemicals company in the world measured by revenues (after [[BASF]], [[Dow Chemical]] and [[LyondellBasell]]). It employs over 15,000 employees at 51 manufacturing plants in 11 countries. In the UK: | ||
| − | INEOS Group | + | :INEOS Group own and run major plant at Runcorn (chlorine and caustic soda, used in many products – pharmaceuticals, synthetic fibres, bleach, water purification etc), Grangemouth in Scotland (two high energy ‘crackers’ to produce commodity chemicals used in fuels, solvents, nylon, packaging etc) and have plants based at Seal Sands, near and linked to the Wilton cluster, in the North East. |
| − | In the | + | It co-owns Grangemouth with [[PetroChina]]. In July 2014 Ineos received a UK government loan guarantee to build Europe’s largest ethane storage tank at Grangemouth. The following month Ineos bought the rights to explore fracking for shale gas in a 127 square mile area around Grangemouth and the Firth of Forth. |
| − | + | In August 2015 Ineos Upstream was awarded a further three blocks (SK45, SK48 and SK58a) by the UK government in its first tranche of the 14th onshore licensing round. | |
| − | + | In January 2018 Ineos announced it was creating six new oil and gas business units 'following the company’s extraordinary 2017 growth'. This has included buying up [[Dong Energy]]’s oil and gas business for $1.05bn in May 2017, and acquiring North Sea interests such as BP's Forties pipeline, making 'a top ten company in the North Sea and the biggest privately-owned exploration and production business operating in North West Europe'. As of January 2018, it had a daily production of around 95,000 boe (barrel of oil equivalent) from assets located in Norway, Denmark and the UK. <ref> Ineos, [https://www.ineos.com/businesses/ineos-shale/news/ineos-launches-six-new-oil-and-gas-businesses/ INEOS launches six new oil and gas businesses], Ineos website, 15 January 2018, accessed 31 January 2018 </ref> | |
| − | == | + | ==The move into shale gas== |
| − | INEOS | + | ===Views=== |
| + | [[File:Ineos frackingsupplement-cover.jpg|right|350px|Ineos PR supplement published in newspapers January 2017]]Back in 2013 INEOS published a lengthy article in its in-house magazine outlining its views on Europe's 'dithering' in the debate over shale gas exploration and production. It argued that action to facilitate shale gas production in the UK is imperative or chemical production in other regions, particularly the US, will gain such a competitive advantage that UK production will become uneconomic. | ||
| − | The firm plans to use imported US shale-derived feedstock in their chemical plants at Grangemouth. INEOS is one of very few companies able to use shale gas as both a fuel and a feedstock. | + | The firm plans to use imported US shale-derived feedstock in their chemical plants at Grangemouth. INEOS is one of the very few companies able to use shale gas as both a fuel and a feedstock. |
| − | :INEOS has decided it cannot wait, and has struck a deal with the US to bring US raw materials to its European plants to maintain a competitive global Olefins & Polymers business. From 2015 INEOS Olefins & Polymers in Norway will begin taking ‘shipments of US-derived ethane – an essential ingredient necessary to produce ethylene. | + | :INEOS has decided it cannot wait, and has struck a deal with the US to bring US raw materials to its European plants to maintain a competitive global Olefins & Polymers business. From 2015 INEOS Olefins & Polymers in Norway will begin taking ‘shipments of US-derived ethane – an essential ingredient necessary to produce ethylene. <ref> Inch Magazine [http://www.ineos.com/inch-magazine/articles/issue-4/material-gain/ Material Gain], 2013 </ref> |
INEOS warned in a report to the [[House of Lords]] EU sub-committee 'that rising energy costs threaten to undermine the ability of manufacturers in the EU to compete on the world stage'. Chemical industries that rely heavily on fossil fuels to run its plants were 'particularly at risk' it said. | INEOS warned in a report to the [[House of Lords]] EU sub-committee 'that rising energy costs threaten to undermine the ability of manufacturers in the EU to compete on the world stage'. Chemical industries that rely heavily on fossil fuels to run its plants were 'particularly at risk' it said. | ||
| − | :'We are acutely vulnerable to fluctuations in energy prices,' said [[Tom Crotty]] | + | :'We are acutely vulnerable to fluctuations in energy prices,' said [[Tom Crotty]], INEOS' group director. 'We sell our products in fiercely competitive international markets and cannot pass on costs to our customers. But we cannot afford to operate in jurisdictions with uncompetitive energy prices.' |
| − | INEOS believes that Europe 'should shield energy-hungry industries from steep price rises' while it moves towards creating affordable low-carbon energy sources. | + | INEOS believes that Europe 'should shield energy-hungry industries from steep price rises' while it moves towards creating affordable low-carbon energy sources. |
:'If it doesn’t, production will be forced out of Europe to more competitive locations which will mean the loss of jobs, investment and tax revenue,' he said. Decarbonisation should not mean deindustrialisation, said Tom. 'The aim must be to connect industry to green energy supplies, not push industry away,” he added. He said energy-intensive industries were not ‘sunset industries’ standing in the way of environmental improvements. 'They are actually a vital source of raw materials and innovations required to make the green economy a reality,' he said. | :'If it doesn’t, production will be forced out of Europe to more competitive locations which will mean the loss of jobs, investment and tax revenue,' he said. Decarbonisation should not mean deindustrialisation, said Tom. 'The aim must be to connect industry to green energy supplies, not push industry away,” he added. He said energy-intensive industries were not ‘sunset industries’ standing in the way of environmental improvements. 'They are actually a vital source of raw materials and innovations required to make the green economy a reality,' he said. | ||
| − | ==Meetings on shale gas with UK government ministers and officials== | + | ===Headquarters move to London=== |
| + | In December 2016, Ineos opened a new headquarters in London, UK, saying the move reflects its increased confidence in this country. | ||
| + | [[Jim Ratcliffe]] said they were 'planning to extract shale gas in the north of England and to grow the newly revitalised Grangemouth. We have immense confidence in Britain’s economic future – the current business climate makes siting our new headquarters in the UK an easy decision. INEOS will continue to grow both in the UK and worldwide. Britain is a good location to ensure both of these goals.' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Climate change and industry minister [[Nick Hurd]] welcomed the company's arrival with open arms, saying: 'This decision is another vote of confidence in the British economy and confirms the company’s commitment to further long-term investment and growth in this country.' <ref> [https://www.energyvoice.com/other-news/126223/126223/ Ineos opens new base in London], ''Energy Voice'', 6 December 2016, accessed 22 December 2016. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Buying up shale exploration licences=== | ||
| + | ====2014==== | ||
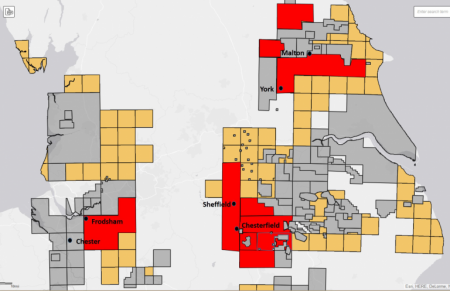
| + | [[File:INEOS-pedl-licences-768x497.png|right|450px]] In August 2014 Ineos made its first move into onshore shale gas exploration in the UK, buying from [[BG Group]] a 51 per cent share of a shale licence covering 329 square km of the Midland Valley in Scotland, which includes the area around the Grangemouth refining and petrochemical complex. [[Dart Energy]] (now owned by [[IGas Energy]]) owned the other 49 per cent <ref> Ineos, [http://www.ineos.com/news/ineos-group/ineos-moves-into-uk-shale-gas-exploration/ INEOS moves into UK shale gas exploration], Press release dated 18 August 2014 </ref> however in March 2015 Ineos announced it was buying IGas's stake in the shale licence around the Grangemouth plant, thus giving it full ownership of the site. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====2015==== | ||
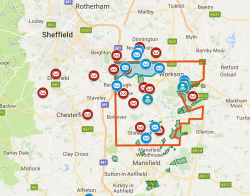
| + | [[File:Ineos licencesAug2017-map.png|left|250px|Click to enlarge]]In March 2015 IGas agreed a deal with chemicals giant [[Ineos]] to sell it at least a 50% interest in seven of IGas’ shale gas licences in the North West along with the option to acquire a 20% interest in two further IGas licences in the East Midlands. The deal is worth £30 million in cash and a further £138 million commitment to fund a two-phase work programme to develop the sites. <Ref> [http://www.ineos.com/news/ineos-group/INEOS/ INEOS to acquire significant share of key IGas North-West shale gas assets], Ineos press release, 10 March 2015, accessed same day </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ineos also pledged an extra £138m to help IGas expand its shale gas operations in the North West and East Midlands regions in England. <ref> [http://www.bbc.com/news/business-31815966 IGas signs £30m shale gas deal with Ineos to expand], ''BBC News'', 10 March 2015, accessed same day </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====2016==== | ||
| + | In September 2016 Ineos was reportedly planning as many as 30 applications for fracking sites in the UK within a year. 'Ineos estimates that it will be at least five years before any of its UK wells are actually producing shale gas'. <ref name=soon> Jana Kasperkevic, [https://www.theguardian.com/business/2016/sep/17/ineos-ohio-frackers-drilling-soon-in-britain In Ohio, frackers are drilling. Soon Ineos will be doing the same in Britain], ''The Guardian'', 17 September 2016. Accessed 22 December 2016. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====2017==== | ||
| + | In March, Ineos bought up 15 shale licences from French energy company [[Engie]] for an undisclosed sum, consolidating its position as the UK's biggest shale gas explorer increasing by 10 per cent its rights to explore across 1.2m acres in the East Midlands, Yorkshire and Cheshire. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Meetings on shale gas with UK government ministers and officials=== | ||
*[[Stephen Lovegrove]], DECC Permanent Secretary met with Jim Ratcliffe on 28 June 2013 at 3 Whitehall Place. The government's briefing notes described Ratcliffe as 'very well connected and has had a number of meetings with Ministers in various Departments and with [[Jeremy Heywood]]'. A section discussing INEOS' potential activities in shale gas was redacted from the briefing note. This meeting appeared to have been suggested to Lovegrove at a 'recent Lancastrian dinner' (held in April 2013). The focus of the meeting was 'primarily... about shale gas and the importance of supporting its development' in the UK. <ref name="DECC"> [https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/275360/14_0127.pdf Email exchanges of 30th June between Ineos and DECC Officials. Briefing material for 28th June Meeting 3. Email exchanges between Ineos and DECC Officials], see page 7 of 17 for this reference. </ref> | *[[Stephen Lovegrove]], DECC Permanent Secretary met with Jim Ratcliffe on 28 June 2013 at 3 Whitehall Place. The government's briefing notes described Ratcliffe as 'very well connected and has had a number of meetings with Ministers in various Departments and with [[Jeremy Heywood]]'. A section discussing INEOS' potential activities in shale gas was redacted from the briefing note. This meeting appeared to have been suggested to Lovegrove at a 'recent Lancastrian dinner' (held in April 2013). The focus of the meeting was 'primarily... about shale gas and the importance of supporting its development' in the UK. <ref name="DECC"> [https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/275360/14_0127.pdf Email exchanges of 30th June between Ineos and DECC Officials. Briefing material for 28th June Meeting 3. Email exchanges between Ineos and DECC Officials], see page 7 of 17 for this reference. </ref> | ||
*[[Duarte Figueira]] (Energy Development) Head of the UK [[Office of Unconventional Gas and Oil]] - with Ineos chairman [[Jim Ratcliffe]] attended the same meeting above. <ref name="DECC"/> | *[[Duarte Figueira]] (Energy Development) Head of the UK [[Office of Unconventional Gas and Oil]] - with Ineos chairman [[Jim Ratcliffe]] attended the same meeting above. <ref name="DECC"/> | ||
| − | *[[Jeremy Heywood]] | + | *[[Jeremy Heywood]], May 2013 met with unnamed representatives of INEOS, [[Cuadrilla]], [[Carillion]], [[UKOOG]], the [[Environment Agency]] and [[Lancashire County Council]] to 'discuss the potential for UK Shale Gas'. <ref> Damian Carrington, [https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2014/jan/17/emails-uk-shale-gas-fracking-opposition Emails reveal UK helped shale gas industry manage fracking opposition], ''The Guardian'', 17 January 2014, accessed 5 January 2017. </ref> <ref> Jeremy Heywood's released external meetings April to June 2013 </ref> He met again in September 2014 with an unnamed representative of INEOS for a further 'discussion on shale gas'. <ref> Jeremy Heywood's released external meetings Q2 2014-2015 </ref> |
| + | *[[James Wharton]], minister for the Northern Powerhouse met with INEOS in September 2015 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Chemical industry meetings with Ministers==== | ||
*[[Michael Fallon]], in November 2013 Ineos met with the [[BIS]] minister as part of a wider group 'to discuss chemical industries'. This included [[Contract Chemicals]], [[Chemical Industries Association]], [[Huntsman]], [[Synthomer]], [[European Chemical Industry Council]] (CEFIC), [[Dow]], [[Thomas Swan and Company]], [[Croda]], [[Verband der Chemischen Industrie]] e.V., [[Solvay]], [[Growhow]], [[Ineos]], [[BASF]]. <ref> Transparency data [https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/313991/october-december-2013-disclosure-ministerial-_meetings.csv/preview BIS ministerial meetings: October to December 2013], Published May 2014, acc 6 November 2013 </ref> | *[[Michael Fallon]], in November 2013 Ineos met with the [[BIS]] minister as part of a wider group 'to discuss chemical industries'. This included [[Contract Chemicals]], [[Chemical Industries Association]], [[Huntsman]], [[Synthomer]], [[European Chemical Industry Council]] (CEFIC), [[Dow]], [[Thomas Swan and Company]], [[Croda]], [[Verband der Chemischen Industrie]] e.V., [[Solvay]], [[Growhow]], [[Ineos]], [[BASF]]. <ref> Transparency data [https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/313991/october-december-2013-disclosure-ministerial-_meetings.csv/preview BIS ministerial meetings: October to December 2013], Published May 2014, acc 6 November 2013 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Attendee at UK energy minister's May 2018 shale gas roundtable==== | ||
| + | Energy minister [[Claire Perry]] hosted a roundtable with the fracking industry just hours before she gave evidence to a committee of MPs on the Conservative government's proposed changes to relax the rules on shale gas development in the UK. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A 'reconstructed' attendee list was released under the freedom of information act to North Yorkshire resident Jonathan Bales following an internal review of the [[Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy]]'s initial almost completely redacted FOI response. <ref> What do they Know?, [https://www.whatdotheyknow.com/request/shale_gas_round_table#incoming-1214895 Shale Gas Round Table: internal review of Freedom of Information request to Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy], 24 July 2018 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Oil and gas companies at the roundtable included: | ||
| + | *[[Aurora Energy]], [[BP]], [[Cuadrilla]], [[IGas]], [[Ineos]], [[Third Energy]] and lobby group [[UK Onshore Oil and Gas]]. | ||
| + | *Service companies: [[Ground Gas Solutions]], [[Marriott Drilling]], [[Onshore Energy Service Group]], [[Zetland Group]]. | ||
| + | *Investors and fund managers: [[Riverstone]] (a major partner in Cuadrilla), [[Kerogen]] (investor in IGas), [[Global Natural Resource Investments]] (formerly part of Barclays which invested in Third Energy), [[KKR]], [[JP Morgan]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other industries and organisations: [[Chemical Industries Association]] chemical company [[SABIC]], [[Coalfield Regeneration Trust]], [[Engineering Employers’ Federation]], [[GMB]]. <ref> Ruth Hayhurst, [https://drillordrop.com/2018/10/22/what-government-told-the-shale-gas-industry-about-success-regulation-jobs-and-support/ What government told the shale gas industry about success, regulation, jobs and support], Drill or Drop, 22 October 2018, accessed same day. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Revolving door=== | ||
| + | ====Secondments of senior civil servants to help develop shale gas strategy==== | ||
| + | In early 2017 Spinwatch revealed that a highly influential senior government official, [[Patrick Erwin]] had been seconded to lead Ineos' strategic push for shale in the UK since 2014. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote style="background-color:#CEF2E0;border:1pt solid Darkgoldenrod;padding:1%;font-size:10pt"> | ||
| + | :One stark example of the fracking industry and government interests aligning is the case of [[Patrick Erwin]], a former top civil servant in the department of energy and climate change (DECC) and the department for communities and local government (DCLG). | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Three years ago, Erwin was seconded to work at Ineos, the petrochemical giant. His move coincided with the firm’s foray into fracking. As Ineos Upstream’s new commercial director, he was central to the development of its shale gas plans, helping it secure over one million acres in government licences to become Britain’s biggest onshore oil and gas operator. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Erwin was Ineos' point-man for its ‘relationship with government and industry’. Documents released to Spinwatch under the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) reveal how in 2014 he organised meetings for Ineos’ billionaire owner, Jim Ratcliffe, with permanent secretary Stephen Lovegrove and other DECC top brass, ahead of the company’s final decision to enter the shale gas market. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :A regular on the shale gas conference circuit, Erwin has argued that fracking is vital for the country’s future. In a speech in summer 2015 he warned that without shale gas the UK risked becoming an environmental ‘theme park'; a strategy he called ‘massively irresponsible’. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :At the same event Erwin acknowledged the importance of talking to and 'standing up in front of communities' in potential shale gas areas. Yet less than a year later he and two other senior Ineos directors held a series of closed private meetings with parish councillors to discuss plans for Ineos license blocks in Cheshire, Derbyshire and North Yorkshire. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Despite FOIA requests, DECC refused to publicly name Erwin as the government’s man seconded to Ineos. Erwin only declared the secondment on his LinkedIn profile after it had ended in 2016. Last month he joined [[Northern Powergrid]] as its policy and markets director. <ref> Melissa Jones, [http://spinwatch.org/index.php/issues/climate/item/5940-meet-the-frackers-a-spinwatch-lobbying-tour Meet the Frackers’: a Spinwatch lobbying tour ], Spinwatch, 15 January 2017 </ref></blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Hiring former PM and business and energy secretary special adviser==== | ||
| + | Later in 2017 Spinwatch also revealed that INEOS's lobbyists [[Burson Marsteller]] had also employed [[Meg Powell-Chandler]], a former PM’s political aide and special adviser to UK business and energy secretary [[Greg Clark]]. Under the broken system regulating the revolving door between big business and politics, the public often has no automatic right to know about such appointments.<ref>Melissa Jones, [http://www.spinwatch.org/index.php/issues/politics/item/5979-time-to-fix-exit-rules-for-special-advisers Time to fix the revolving door rules for special advisers], Spinwatch, 17 October 2017 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Lobbying against green energy taxes=== | ||
| + | In April 2017 it emerged Ineos was pushing the government to use Brexit as a chance to exempt the chemicals sector entirely from climate policy costs. Documents obtained by Friends of the Earth revealed that an industry-government initiative [[Chemistry Growth Partnership]] chaired by Ineos director Tom Crotty, was lobbying to get rid of the UK’s carbon floor price ( a carbon tax on electricity generators) as part of their efforts to cut energy costs passed on to chemical companies. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The objective, as revealed in the documents, is to: 'Support appropriate policies to enable the safe exploitation of unconventional gas [shale gas], sustainable use of biofuels and optimal use of waste resources.'<ref>Adam Vaughan, [https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2017/apr/03/ineos-leads-lobbying-effort-to-get-out-of-paying-green-tax Fracking firm Ineos leads industry lobbying to avoid green tax], The ''Guardian'', 3 April 2017 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bullying tactics: threatens to sue the National Trust if it doesn't agree to seismic surveys=== | ||
| + | In July 2017 Ineos said that it had been trying to get permission to carry out seismic surveys in Nottinghamshire's historic Clumber Park from the [[National Trust]] for over a year, but claimed that the Trust had refused to discuss and so Ineos was considering legal action. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :If the National Trust refuses to change its position, Ineos will have no choice but to write to the [[Oil and Gas Authority]], asking for permission to seek a court order enforcing its rights to carry out these surveys on National Trust land,” Ineos said in a statement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Director [[Tom Crotty]] argued that Ineos's ability to extract shale gas would be 'significantly limited' if tests could not be carried out on the Trust's land. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ineos Shale's commercial director [[Lynn Calder]] claimed the Trust was playing politics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | : 'The National Trust is taking an overtly political position against all fossil fuels. What it fails to recognise is that shale gas is 50% cleaner than coal and 30 per cent cleaner than oil. The development of shale gas will actually reduce greenhouse gas emissions. We are developing a shale gas industry that is safe and essential for the UK and the economy. It is estimated that the industry will create tens of thousands of well-paid jobs and Ineos has pledged to give 6 permission of revenue to local people - potentially amounting to billions of pounds.” <ref> Alan Jones, [http://www.independent.co.uk/news/business/news/ineos-national-trust-fracking-lawsuit-energy-firm-legal-action-clumber-park-nottinghamshire-seismic-a7851581.html Ineos threatens to sue National Trust so it can carry out fracking survey on its land], ''Independent'', 20 July 2017, accessed 21 August 2017 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In a statement announcing the application submission, INEOS said it believes the trust has 'behaved unreasonably', adding that 'it is firmly in the national interest and a court order would back our position'. [[Rob Coyle]], Ineos Shale's chief executive, accused the Trust of ‘failing to engage with us or the science’ and even warned that it will withhold profits from the Trust for being obstructive, if it does eventually win permission. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In January 2018 the ''Telegraph'' reported that the National Trust had sent a 'heartfelt letter' to INEOS asking it to abandon Clumber Park survey plans. Beth Dawson General manager of National Trust Clumber Park invited INEOS staff to visit the Grade-1 listed parkland, which is a designated site of special scientific interest, receives half a million visitors a year, and has a number of internationally protected species of birds. <ref> Sarah Knapton, [http://www.telegraph.co.uk/science/2018/01/07/national-trust-sends-heartfelt-letter-fracking-company-asking/ National Trust sends heartfelt letter to fracking company asking it to abandon Clumber Park survey plans], Telegraph.co.uk, 7 January 2018 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Hiring ex-MPs to write PR booklets=== | ||
| + | In December 2017 INEOS Shale controversially commissioned the former North East Derbyshire MP [[Natascha Engel]] to write an 'information 'booklet' which would 'better explain shale exploration and development' and would be distributed to locals in the areas where it was applying to drill for shale gas, such as Marsh Lane, near Eckington. Operations director [[Tom Pickering]] explained that Engel's assistance would 'give us a better insight into the needs and concerns of residents. As a former Labour MP and trade unionist, Natascha has always made the case for good jobs, as well as health and safety. At the same time, Natascha is well placed to give us a full understanding of local issues and help us to continue to be an open and inclusive organisation.' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Engel explained her rationale to carry out this work in INEOS's press release: | ||
| + | : I saw first-hand what the impacts are on small communities when they hear about a shale gas application near them – even when it’s only for exploratory drilling. What people want is information. They want to know how it will affect them and they want reassurance that it is safe. I hope that this booklet will provide some of those certainties. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Most of all I hope that this will allow INEOS to work constructively with communities so that local people gain the most in terms of the jobs and apprenticeships that this industry could bring – something I have campaigned on for most of my adult life. <ref> [https://www.ineos.com/businesses/ineos-shale/news/ineos-shale-commission-former-mp-natascha-engel/ INEOS Shale commission former MP Natascha Engel], INEOS Shale, 1 December 2017, accessed Dec 2017, and 7 Jan 2018 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Engel's decision was criticised by several Labour MPs. [[Anne Western]], leader of Derbyshire Labour Group said: 'Natascha Engel’s decision to work on behalf of Ineos is shocking and disappointing. Natascha’s views on fracking are entirely her own and do not represent Labour Party policy or the views of many Labour members.'
| ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Dennis Skinner]] the Labour MP for Bolsover said: 'The Labour Party is totally against fracking. Our policy, adopted at the party conference in 2016, is to ban fracking completely in the UK and to back clean technologies and renewable energy.
I have been campaigning against fracking locally and in Parliament. I recently raised the matter with Theresa May at PMQs because of the water contamination at Oxcroft.
Unlike [[Lee Rowley]], who made it clear last week during a Westminster Hall debate that he doesn’t oppose fracking in principle, only in north-east Derbyshire, I am against fracking wherever it is proposed.'<ref> [https://www.derbyshiretimes.co.uk/news/decision-by-former-mp-to-link-up-with-fracking-firm-criticised-1-8895362 Decision by former MP to link up with fracking firm criticised], ''Derbyshire Times'', 6 December 2017 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Injunction against potential protesters at its sites== | ||
| + | [[File:Injunction-notice TF resized.jpg|450px|right]] In July 2017 Ineos Shale secured an interim High Court injunction against anti-fracking protestors<ref> Upstream Limited and others v Persons Unknown Approved Note of Judgment of Mr Justice Morgan dated 28 July 2017 </ref> at a private hearing with no members of the public or press present. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Operations director [[Tom Pickering]] told the Press Association that the move by INEOS was not an attempt to quash peaceful protest but instead taken for safety reasons. He said: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :'I have a duty of care to the employees, contractors and public at large that is in the health and safety act as written words to ensure and protect their safety and that includes a protester. As I plan for my operations, I can see all the unlawful protest that has happened. Real extreme and dangerous protest. Lorry surfing, releasing loads, blocking up a high way – all of these types of things, which are criminal acts anyway. But I think it had not been addressed with a very clear line of what is acceptable and what is not. What I want to be clear on is that we constantly respect peaceful protest. Nothing about Ineos Shale is going to stop listening to people and engaging with people.” <Ref>Press Association, [https://www.energyvoice.com/oilandgas/148703/brexit-vote-sparked-shift-tone-fracking-says-ineos-boss/ Brexit vote sparked ‘shift in tone’ on fracking, says Ineos boss], Energy Voice, 27 August 2017, accessed 28 August 2017 </ref> | ||
| + | ==='Draconian, anti-democratic and oppressive’=== | ||
| + | Campaigners described the move by Ineos and the courts as ‘draconian, anti-democratic and oppressive’. The high-profile group Talk Fracking, accused INEOS of trying to privatise the law, saying: ‘If this injunction is allowed to stand, it will mean that any corporation can apply for a 'pre-emptive injunction' of this nature to prevent any protest by 'persons unknown' at any site in the future, citing the INEOS injunction as a precedent. This, in effect, could shut down peaceful protest across the UK, or at least make it far more difficult to organise without running the risk of draconian punishment.’
| ||
| + | |||
| + | Campaigners challenged the injunction at a court hearing in September 2017, but the judge ruled in the chemical giant's favour for it to continue. During the hearing, it emerged that INEOS had amassed thousands of pages of Facebook posts and tweets as evidence that it faced ‘a real and imminent threat’ of being targeted by unlawful protests.<ref name="draconian"> Andy Rowell, [http://spinwatch.org/index.php/issues/climate/item/5987-exclusive-fight-against-ineos-draconian-injunction-goes-to-the-court-of-appeal Exclusive: Fight against INEOS' ‘draconian’ injunction goes to the Court of Appeal], Spinwatch, 19 January 2018 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The company behind the Facebook surveillance was private security contractors [[Eclipse Strategic Security]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Campaigners take case to Court of Appeal=== | ||
| + | In January 2018 anti-fracking campaigner, Joe Corré, announced he was taking his legal case against Ineos to the Court of Appeal. Legal papers lodged with the court argue that the ‘learned judge erred in law by permitting a claim for injunctive remedies against 'Persons Unknown', as well as ‘wrongly prohibiting conduct which is lawful’. Corre's legal team also contend that the injunction breached the Court's obligations under Section 6 of the Human Rights Act and Articles 8, 10, and 11 of the European Convention on Human Rights. <ref name="draconian"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Victory for campaigners=== | ||
| + | [[FILE:JoeCorre-Talking-Fracking-April19.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Anti-fracking campaigner Joe Corre celebrates victory at the Court of Appeal. Credit: DrillorDrop]] In April 2019 three Court of Appeal judges finally ruled in favour of anti-fracking activists Joe Corre and Joe Boyd to overturn INEOS' sweeping and draconian injunction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In granting the appeal, Lord Justice Longmore and two other judges ruled that INEOS' initial injunction was “too wide and insufficiently clear” and that the judge who granted the injunction had “attempted to do the impossible” - making an order that was “too wide and too uncertain”. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The judges discharged part of the original injunction relating to demonstrations in public areas and protesters combining together with the intention of damaging Ineos, which campaigners argued was having a serious effect on lawful and legitimate protest activities. According to Longmore, “The citizen’s right of protest is not to be diminished by advance fear of committal except in the clearest of cases.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | Two other aspects of the injunction remain, pending reconsideration by the high court of whether the campaigners’ right to freedom of expression as outlined in the Human Rights Act would be restricted. Reacting to the ruling INEOS boss Tom Pickering told the media: “We are talking with our legal team about our next steps, because we believe it is essential that the forces of law and order prevail. We respect peaceful protest, but we must stand up to the militants who game the legal system with intimidation and mob rule. We stand for jobs and opportunity. They stand for anarchy in the UK.”<ref> Rob Evans, [https://www.theguardian.com/law/2019/apr/03/protesters-hail-legal-victory-over-fracking-firms-injunction Protesters hail legal victory over fracking firm's injunction', The ''Guardian'', 3 April 2019, accessed same day. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Campaigner Joe Corre said: "Today's win is a fantastic result and has restored my confidence in the British Legal system. INEOS thought they could game the British legal system by using ASBO laws designed to protect people, against the people. They can think again!" <ref> Ruth Hayhurst, [https://drillordrop.com/2019/04/03/breaking-anti-fracking-campaigners-win-appeal-against-ineos-protest-injunction/amp/?__twitter_impression=true Breaking: Anti-fracking campaigners win appeal against Ineos protest injunction], DrillorDrop, 3 April 2019. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Fracking in Scotland== | ||
| + | In 2015 Ineos launched a 'Scottish shale gas community engagement programme' to help tackle the opposition that has emerged against fracking in the region. Its campaign, dubbed 'love bombing' by campaigners, aimed to persuade people that fracking technology was safe, and how the process could bring huge economic benefits to locals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The petrochemical company's sudden concern for the nation's economic performance was considered somewhat perplexing, given the Grangemouth controversy that had erupted just a few months earlier, when Ineos chose to keep its plant shut despite the cancellation of the planned strikes - actions that saw it accused of holding Scotland 'to ransom'.<ref> [http://static1.squarespace.com/static/56057a6fe4b0ba7911a449d6/t/561982a6e4b01839b1bbc5a3/1444512422921/Scottish_Lobbying_Guide.pdf Holyrood Exposed: A Guide to Lobbying in Scotland], squarespace.com, 12 October 2015, accessed 12 October 2015 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Scotland has had a moratorium on shale gas, coal bed methane and underground coal gasification since 2015. In June 2016 when the Scottish Parliament voted for a permanent ban Ineos responded by stating that the vote made little difference. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :'The vote this evening changes very little. A process remains in place in Scotland to further assess scientific, evidence-based research before a decision is taken on fracking. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :This has important implications for the people of Scotland and its economy and should not be prejudged before it has reached its conclusion. INEOS has been clear that it believes shale gas can be extracted safely and that Scotland is losing out as the centre of excellence moves south. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :We are focused on England where we believe that shale can provide much-needed jobs, investment and energy security.' <ref> [https://twitter.com/INEOS_Upstream INEOS Upstream], Twitter </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Meetings with ministers==== | ||
| + | *28 January 2015 - First Minister [[Nicola Sturgeon]] met with INEOS chairman [[Jim Ratcliffe]] on the same day that energy minister [[Fergus Ewing]] announced a Scottish moratorium on fracking. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *21 June 2017 - Senior Scottish ministers held private meetings with INEOS and Grangemouth executives from China five times in 13 months, reports Rob Edwards at ''The Ferret''. Briefings released under freedom of information law show that in 2016 Nicola Sturgeon met Ineos boss [[Jim Ratcliffe]] and Chinese businessmen who are involved in helping to run the Grangemouth refinery. The Deputy First Minister John Swinney and economy secretary Keith Brown also met with Ineos managers. The purpose of the meetings has been kept secret.<ref> Rob Edwards, [https://theferret.scot/scottish-ministers-fracking-firm-ineos/?utm_source=push Revealed: Scottish ministers’ meetings with fracking firm] ''The Ferret'', June 21, 2017 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====PR films countering anti-fracking concerns==== | ||
| + | *INEOS, [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_8aMpw2H6sc&feature=youtu.be Fracking facts water contamination]: 'Some campaigners claim fracking leads to water contamination. That is not the case. This video explains the facts.' Published on Youtube May 2016. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *In September 2016 it was reported that '[a]s part of its campaign to win over critics, Ineos invited journalists to tour fracking sites in Pennsylvania operated by [[Consol]], a Pittsburgh-based producer of natural gas and coal and, supposedly, an example of why fracking will be good for the UK.' <ref name=drilling> Jana Kasperkevic, [https://www.theguardian.com/business/2016/sep/17/ineos-ohio-frackers-drilling-soon-in-britain In Ohio, frackers are drilling. Soon Ineos will be doing the same in Britain], ''The Guardian'', 17 September 2016. Accessed 22 December 2016. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====First shipment of shale gas==== | ||
| + | [[Image:Ineos Shale Gas Ship 171783307.jpg|thumb|500px|right|Ineos tanker on the Forth en route to Grangemouth in Scotland, 2016]]In September 2016, a tanker carrying ethane from the US sailed up the Forth to the Ineos refinery in Grangemouth. Ineos said the shipment was the result of a £1.6billion investment in eight tankers that will form a 'virtual pipeline' for shale gas between the US and the UK and Norway. 'The Intrepid' - its smaller sibling, the INEOS Insight, was the one to dock in Forth - is one of four Dragon-class vessels that have already been delivered to Ineos. Over the next year, another four will be built and launched. <ref> [http://www.offshore-technology.com/features/featureus-shale-tsunami-to-hit-europes-shores-5688052/ Shale tsunami: the virtual pipeline funnelling oil to Europe's shores], ''Offshore Technology'', 19 December 2016, accessed 22 December 2016. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ineos claims the gas will replace dwindling North Sea supplies, and secure the future of Grangemouth’s 1300 workforce, and a further 9000 Scottish jobs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When the shipment arrived, many politicians and environmental groups criticised the gas, fearing it will be a first step on the road to allowing fracking in Scotland. | ||
| + | [[Mark Ruskell]] MSP, the [[Scottish Greens]]' climate, energy and environment spokesman, said: | ||
| + | :'As well as shale gas, the so-called 'dragon' fleet of ships docking in Scotland will also bring with them a renewed campaign by Ineos for fracking to be given the go ahead. The Scottish Government must legislate for an outright ban on fracking because its vague 'moratorium' policy is clearly giving hope to fossil fuel giants intent on digging up Scotland.' <ref> [http://www.dailyrecord.co.uk/news/scottish-news/first-shipment-shale-gas-arrives-8921255 First shipment of shale gas from US arrives in Grangemouth, met by angry environmentalists], ''Daily Record'', 27 September 2016. Accessed 22 December 2016. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =====PR Junket for journos to greet the US shale gas supertanker arrival===== | ||
| + | INEOS wined and dined journalists and paid for their 4-star hotel overnight stays in Edinburgh plus return flights to the city, as part of a PR junket to promote the arrival of its super gas tankers from the US. Scottish investigative site ''The Ferret'' reported that INEOS was due to host a dinner at the Wedgwood restaurant, with breakfast the following morning on a boat on the Firth of Forth ahead of meeting the gas tanker INEOS Insight. Longstanding INEOS PR company [[Media Zoo]] organised the junket. The event received extensive press coverage across the UK. <ref>Ferret Journalists, [https://dropping.theferret.scot/ineos-pr-fracking-gas-boat/ INEOS PR plan to greet fracking boat], The Ferret, September 26, 2016 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Responses to the Scottish Government report and moratorium==== | ||
| + | On the Scottish Government's decision to impose both a report and moratorium on fracking, Ratcliffe said: 'We have no objection to people evaluating safety and environmental issues, I think that’s all very fair and proper. But it probably would have been quite sensible to let us at least do the exploration phase in Scotland.' <ref> [http://www.dailyrecord.co.uk/news/scottish-news/first-shipment-shale-gas-arrive-8916565 First shipment of US shale gas to arrive in Scotland as fracking debate continues], ''Daily Record'', 26 September 2016. Accessed 22 December 2016. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | One of the biggest fears of the Scottish government regarding shale gas is the lack of regulation shown in the US. In September 2016, Ineos insisted that fracking in the UK will be different than in the US. It argued that technology has come a long way over the past decade. Also, as the US fracking industry has matured, lessons were learned, making it easier to replicate best practices on fracking sites in the UK. To ease the inconvenience of light, noise and traffic during drilling, Ineos also promised to give 6% of its profits to the UK communities where it will frack. <ref name=soon> Jana Kasperkevic, [https://www.theguardian.com/business/2016/sep/17/ineos-ohio-frackers-drilling-soon-in-britain In Ohio, frackers are drilling. Soon Ineos will be doing the same in Britain], ''The Guardian'', 17 September 2016. Accessed 22 December 2016. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 2018, Ineos took Scottish ministers to court for introducing what it deemed was an 'effective ban' on fracking in the form of the moratorium. The court dismissed Ineos' multi-million damages claim however concluded that the Scottish Government had not banned fracking. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===APPG Debate on fracking in Scotland=== | ||
| + | In a debate hosted by the All Party Parliamentary Group on Unconventional Oil and Gas (APPGUOG) in December 2016, [[Stephen Tindale]], now a consultant to INEOS Shale, defended the idea of fracking in Scotland. He argued that '[s]hale is a necessary part of decarbonisation' as the demand for gas-based sources of heating will remain high for several decades. Tindale also argued that, while shale gas extraction did not have a public license now, it did have a human rights element to it as it would mean less dependency on imports from states who do not respect the human rights of their people. He responded to the argument that fracking destroyed jobs in other sectors such as renewables and conventional oil and gas by blaming the government instead for its erratic policies on renewables. | ||
| + | |||
| + | On the question of whether shale gas extraction is beneficial to the economy, Tindale said: | ||
| + | :'Nobody knows because the geology of the UK is very different from the US so it needs to be tested. Is that a waste of money? It might be. The question then is whose money is it? Is it public money? No. [...] [W]e shouldn’t give public money to it but we should be prepared to allow them [the companies] to proceed [investments] if they have their own money. <ref> [ http://www.theenergycollective.com/energy-post/2394513/fracking-gang-plank-to-climate-chaos-or-necessary-part-of-decarbonization Fracking: ‘Gang Plank to Climate Chaos’ or ‘Necessary Part of Decarbonization’?], ''Energy Collective'', December 7, 2016, accessed December 22, 2016. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Ineos PEDL licence extended in 2019 for the second time === | ||
| + | |||
| + | On 1 July 2019 the Scottish Government renewed an onshore petroleum exploration and development licence PEDL 162, which is 80 per cent owned by Ineos and permits fracking and other underground gas extraction technologies. The licence covers 400sq km to the south and west of Falkirk, and was extended for another year. It had already been extended for one year from July 2018. Reach Coal Seam Gas owns the other 20 per cent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to the Ferret: | ||
| + | :PEDL 162 was originally granted by the Westminster government to a firm called [[Reach Coal Seam Gas]] in 2008. Ineos bought four-fifths of the licence in 2014, and responsibility for licensing was devolved to Holyrood in February 2018. <ref> Rob Edwards, [https://theferret.scot/pedl-162-ineos-fracking-licence-renewed/ | ||
| + | Scottish Government move to renew Ineos fracking licence ‘disappointing’], The Ferret, 1 July 2019, accessed same day </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reach Coal Seam Gas's own press release in 2014 announcing it had farmed out 80 per cent of the licence to Ineos states that it had previously 'conducted extensive geological studies which have shown PEDL162 may contain large amounts of producible hydrocarbons'. <ref> Reach CSG, [http://www.reachcsg.co.uk/press-releases-for-reach-csg.html Press Releasee], 13 October 2014, accessed 1 July 2019 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Campaign groups and communities were dismayed by the announcement of the license extension reports The Ferret. However Scottish energy minister [[Paul Wheelhouse]] argued in a letter released 28 June that: “It would have been a dereliction of our responsibility as a competent licensing authority not to consider the request for an extension, taking into account all the relevant factors.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | The decision followed a request submitted by the licensees said Wheelhouse, and a second round of extended consultations on the environmental and business impact of the government’s opposition to fracking which concluded 25 June 2019. The extension to PEDL 162 would give time for the policymaking process to conclude and for licensees to consider their position, Wheelhouse argued. <ref> Rob Edwards, [https://theferret.scot/pedl-162-ineos-fracking-licence-renewed/ | ||
| + | Scottish Government move to renew Ineos fracking licence ‘disappointing’], The Ferret, 1 July 2019, accessed same day </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Constituencies including INEOS licences== | ||
| + | *Altrincham and Sale West - [[Graham Brady]] | ||
| + | *Amber Valley - [[Nigel Mills]], MP Conservative | ||
| + | *Ashfield Co - [[Gloria de Piero]] | ||
| + | *Barnsley Central - [[Dan Jarvis]] | ||
| + | *Barnsley East – [[Michael Dugher]] | ||
| + | *Bassetlaw - [[John Mann]] | ||
| + | *Bolsover - [[Dennis Skinner]] | ||
| + | *Chesterfield - [[Toby Perkins]] | ||
| + | *Congleton - [[Fiona Bruce]], MP Conservative | ||
| + | *Derbyshire Dales - [[Patrick McLoughlin]], MP Conservative | ||
| + | *East Yorkshire - [[Greg Knight]] | ||
| + | *Eddisbury - [[Antoinette Sandbach]] | ||
| + | *Halton - [[Derek Twigg]] | ||
| + | *Macclesfield - [[David Rutley]] | ||
| + | *Mansfield - [[Alan Meale]] | ||
| + | *NE Derbyshire - [[Natascha Engel]] (Labour) until June 2017, replaced by Conservative [[Lee Rowley]]. Engel was later contracted by Ineos to write a report on shale gas development. She also was appointed the UK's first ever shale gas commissioner in October 2018, but had resigned by April 2019 over the government's refusal to revisit the regulations over seismic levels during shale gas operations. | ||
| + | *Newark - [[Robert Jenrick]] | ||
| + | *Penistone and Stockbridge - [[Angela Smith]], MP Conservative | ||
| + | *Richmond (Yorks) - [[Rishi Sunak]] | ||
| + | *Rother Valley - [[Kevin Barron]] - includes the Harthill and Woodsetts sites. By June 2018 Hartill had received permission, and a revised Woodsetts application had been re-submitted. | ||
| + | *Rotherham - [[Sarah Champion]] | ||
| + | *Scarborough and Whitby – [[Robert Goodwill]], MP Conservative | ||
| + | *Sheffield Central - [[Paul Blomfield]] | ||
| + | *Sheffield Hallam - [[Nick Clegg]] | ||
| + | *Sheffield SE - [[Clive Betts]] | ||
| + | *Sheffield, Brightside and Hillsborough - [[Gill Furniss]] | ||
| + | *Sheffield, Heeley - [[Louise Hay]] | ||
| + | *Sherwood - [[Mark Spencer]] | ||
| + | *Tatton - [[George Osborne]], MP Conservative | ||
| + | *Thirsk and Malton - [[Kevin Hollinrake]], MP Conservative | ||
| + | *Warrington South - [[David Mowat]] | ||
| + | *Weaver Vale - [[Graham Evans]] | ||
| + | *Wentworth and Dearne - [[John Healey]] | ||
| + | *York Central - [[Rachael Maskell]] | ||
| + | *York Outer - [[Julian Sturdy]] | ||
==Legal action against Chinese companies over misuse of trade secrets== | ==Legal action against Chinese companies over misuse of trade secrets== | ||
In March 2014 Ineos announced it was taking legal action against a number of [[Sinopec]] and Sinopec subsidiaries ([[SNEC]], [[Anqing]] and others) for breach of contract and/or misuse of trade secrets. | In March 2014 Ineos announced it was taking legal action against a number of [[Sinopec]] and Sinopec subsidiaries ([[SNEC]], [[Anqing]] and others) for breach of contract and/or misuse of trade secrets. | ||
| − | :INEOS says that Sinopec Ningbo Engineering Company has broken a long established technology agreement which, together with trade secret misuse by other Sinopec companies, has enabled development of a series of new world scale Acrylonitrile plants without INEOS agreement or consent. INEOS, which has otherwise excellent relationships with Sinopec and with China, has no choice other than to protect its intellectual property. INEOS fears that these breaches of rights will cause major harm to its Acrylonitrile business which generates up to $500m per annum of profit and has a replacement value of $3 billion. It supports around 5,000 direct and indirect jobs in the USA and Europe. <ref> [http://www.ineos.com/news/ineos-group/protect-ineos-ip/ INEOS announces legal action against Sinopec and Sinopec subsidiaries], 21 March 2014, acc 5 May 2014 </ref> | + | :INEOS says that Sinopec Ningbo Engineering Company has broken a long established technology agreement which, together with trade secret misuse by other Sinopec companies, has enabled development of a series of new world-scale Acrylonitrile plants without INEOS agreement or consent. INEOS, which has otherwise excellent relationships with Sinopec and with China, has no choice other than to protect its intellectual property. INEOS fears that these breaches of rights will cause major harm to its Acrylonitrile business which generates up to $500m per annum of profit and has a replacement value of $3 billion. It supports around 5,000 direct and indirect jobs in the USA and Europe. <ref> [http://www.ineos.com/news/ineos-group/protect-ineos-ip/ INEOS announces legal action against Sinopec and Sinopec subsidiaries], 21 March 2014, acc 5 May 2014 </ref> |
==Affiliations== | ==Affiliations== | ||
| − | *[[All Party Parliamentary Group on Unconventional Oil and Gas]] - Ineos | + | *[[All Party Parliamentary Group on Unconventional Oil and Gas]] - Ineos was an associate member, as well as a member of the 'independent advisory panel' of this controversial APPG. Its first contribution was £10,000, which was registered in June 2013. The APPG ceased four years later, following the 2017 general election. It was administered by two big lobbying agencies during its operation: [[Edelman]] and [[Hill and Knowlton]]. |
*[[Parliamentary and Scientific Committee]] (an [[Associate Parliamentary Group]]) | *[[Parliamentary and Scientific Committee]] (an [[Associate Parliamentary Group]]) | ||
| Line 48: | Line 271: | ||
*[[Jim Ratcliffe]] - founder and chairman | *[[Jim Ratcliffe]] - founder and chairman | ||
*[[Tom Crotty]] - INEOS group and external affairs director | *[[Tom Crotty]] - INEOS group and external affairs director | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Tom Pickering]] - chief financial officer |
*[[Andrew McLachlan]] - senior account director | *[[Andrew McLachlan]] - senior account director | ||
| − | *[[Peter Rose]] - business development director | + | *[[Peter Rose]] - business development director, speaker at ShaleWorld UK conference |
| − | *[[Gary Haywood]], CEO of INEOS Upstream | + | *[[Gary Haywood]], CEO of [[INEOS Upstream]] and in charge of leading the company’s fracking plans |
| + | *[[John McNally]], chief executive of Ineos’s UK petrochemicals arm | ||
| + | *[[David East]], communications manager | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Former executives=== | ||
| + | *[[Patrick Erwin]], commercial director of Ineos Upstream, leading on commercial strategy, developing partnerships and on asset purchase - led the economics and work programme parts of for INEOS’s application to the 14th Onshore Licensing Round. Seconded from central government 2013-May 2016, then on staff until December 2016 before leaving to join Northern Powergrid. | ||
| + | *[[Calum MacLean]] - a founder member of INEOS in 1998 and chairman O&P Europe and chief executive officer [[O&P Europe]] (UK) since 2011. He left to join rival chemical company [[Synthomer]] in January 2015. Several months later Ineos COO [[Steve Bennett]] also joined the company. <ref> Joanna Burke, [http://www.independent.co.uk/news/business/news/ineos-boss-to-sue-former-right-hand-man-for-hiring-in-breach-of-terms-10150615.html Ineos boss to sue former right-hand man for hiring 'in breach of terms'], The Independent, 2 April 2015 </ref> | ||
==Lobbying and PR firms== | ==Lobbying and PR firms== | ||
===External=== | ===External=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{#ev:youtube|https://youtu.be/toTLr2yIJ5E|450|right|''Watch 'Meet the Frackers: a Spinwatch lobbying tour'''' to find out more about the lobbyists INEOS hires to help it push fracking in the UK''}} *[[Burson-Marsteller]] (B-M) took over the Ineos account in July 2014 from [[Portcullis Public Affairs]] who had retained it for several years. Freedom of information requests reveal that B-M has set up meetings with UK government ministers for INEOS. In 2017 B-M hired [[Meg Powell-Chandler]], a former special adviser to business and energy minister [[Greg Clark]] and former prime minister [[David Cameron]]. <ref> *Melissa Jones, [http://www.spinwatch.org/index.php/issues/politics/item/5979-time-to-fix-exit-rules-for-special-advisers Time to fix the revolving door rules for special advisers], Spinwatch, 17 October 2017 </ref> In June 2018 Trade industry magazine PRWeek reported that B-M was no longer handling Ineos's account. | ||
| + | *[[PPS Group]] provides public affairs advice to Ineos Enterprises Ltd (2014-2015) | ||
| + | *[[Media Zoo]]’s UK media relations and reputation management brief includes communicating with trade organisations and governments in the US and Germany, which are key markets for Ineos. <ref> Glen Munro, Grangemouth owner Ineos awards corporate work to Media Zoo, prweek.com, 21 January 2014 </ref> Creative director [[Mark Killick]] works on the Ineos account. <ref>Mark Killick, [http://www.prweek.com/article/1226182/comms-battle-grangemouth The comms battle for Grangemouth], ''PRWeek'', January 07, 2014, acc 20 August 2014</ref> along with [[Andrew McLachlan]] and [[Hannah Brandstaetter]]. Media Zoo has also facilitated press trips from the UK to view the company's operations in the US | ||
| + | *[[Edelman]] <ref> PRCA Public Affairs Register: Consultancies – March to May 2013 </ref> | ||
===Internal=== | ===Internal=== | ||
*[[Richard Longden]] (INEOS) | *[[Richard Longden]] (INEOS) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Contact== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :Website: http://www.ineos.com/ | ||
| + | :Twitter: [https://twitter.com/INEOS_Upstream @INEOS_Upstream] | ||
| + | |||
| + | :London address: 38 Hans Cres, London SW1X 0LZ | ||
==Resources== | ==Resources== | ||
| − | * | + | ===On Powerbase and Spinwatch=== |
| − | * | + | See: [[Fracking lobbying firms]] |
| + | See: [[Fracking Spads]] | ||
| + | *Melissa Jones and Andy Rowell, [http://www.spinwatch.org/index.php/issues/climate/item/5765-access-all-areas-frackers-lobbyists-and-the-revolving-door Access all areas: Westminster's (vast) fracking lobby exposed], 29 April 2015. | ||
| + | *Video: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=toTLr2yIJ5E Meet the Frackers: a Spinwatch lobbying tour], ''Spinwatch | YouTube'', 16 January 2017. | ||
| + | *Andy Rowell, [http://spinwatch.org/index.php/issues/climate/item/5970-slapps-and-aggressive-cold-calling-how-ineos-is-selling-shale SLAPPS and ‘aggressive cold calling’: How INEOS is selling shale], Spinwatch August 2017 | ||
| + | *Melissa Jones, [http://www.spinwatch.org/index.php/issues/politics/item/5979-time-to-fix-exit-rules-for-special-advisers Time to fix the revolving door rules for special advisers], Spinwatch, 17 October 2017 | ||
| + | *Andy Rowell, [http://spinwatch.org/index.php/issues/climate/item/5987-exclusive-fight-against-ineos-draconian-injunction-goes-to-the-court-of-appeal Exclusive: Fight against INEOS' ‘draconian’ injunction goes to the Court of Appeal]. Spinwatch, 19 January 2018 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Ineos=== | ||
| + | '''Ineos Public relations video series''' | ||
| + | :*Video: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SR5IpI7ALfc Why do we need fracking?], ''YouTube - INEOS Group'', 13 May 2016 | ||
| + | :*Video: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=v1tzWX1ZCFQ Fracking facts what is fracking], ''YouTube - INEOS Group'', 13 May 2016 | ||
| + | :*Video: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_8aMpw2H6sc Fracking facts water contamination], ''YouTube - INEOS Group'', 13 May 2016 | ||
| + | :*Video: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=00iL2rO4F-8 Fracking facts earthquakes], ''YouTube - INEOS Group'', 13 May 2016 | ||
| + | :*Video: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ikulUa9I82U Fracking facts air quality], ''YouTube - INEOS Group'', 13 May 2016 | ||
| + | :*Video: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8rVQO6cutcI Fracking facts chemicals], ''YouTube - INEOSGroup'', 13 May 2016 | ||
| + | *[https://www.youtube.com/user/INEOSgroup INEOS YouTube channel], ''YouTube - INEOS Group'' | ||
| + | ====PR supplements==== | ||
| + | *Ineos, [[File:Ineos-fracking-supplement-2017.pdf |Fracking, What everyone should know]], advertising feature pull-out, this version published in the Derbyshire Times,28 January 2017 [pdf download] | ||
| + | |||
===Freedom of information requests=== | ===Freedom of information requests=== | ||
*[https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/275360/14_0127.pdf Letter regarding FOI request on INEOS introductory meeting with DECC Permanent Secretary June 2013], [[Office of Unconventional Gas and Oil]] (OUGO), dated 27 January 2014, acc 5 May 2014 | *[https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/275360/14_0127.pdf Letter regarding FOI request on INEOS introductory meeting with DECC Permanent Secretary June 2013], [[Office of Unconventional Gas and Oil]] (OUGO), dated 27 January 2014, acc 5 May 2014 | ||
*Emails, [https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/275360/14_0127.pdf Email exchanges of 30th June between Ineos and DECC Officials. Briefing material for 28th June Meeting 3. Email exchanges between Ineos and DECC Officials] | *Emails, [https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/275360/14_0127.pdf Email exchanges of 30th June between Ineos and DECC Officials. Briefing material for 28th June Meeting 3. Email exchanges between Ineos and DECC Officials] | ||
| − | == | + | ====News articles and video==== |
| + | *Letter to the Editor [http://www.theguardian.com/politics/2013/oct/21/ineos-tax-china Ineos, tax and China], ''The Guardian'', Monday 21 October 2013 21.00 BST | ||
| + | *[http://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/newsbysector/energy/oilandgas/10489613/US-shale-gas-plan-to-make-Grangemouth-profitable.html US shale gas plan to make Grangemouth profitable], The Telegraph, 2 September 2013 | ||
| + | *Simon Goodley, [http://www.theguardian.com/environment/2014/sep/28/british-firm-ineos-accused-bribes-bulldozers-approach-frackingBritish firm Ineos accused of ‘bribes and bulldozers’ approach to fracking], ''The Guardian'', 28 September 2014 | ||
| + | *Nick Mathiason, [http://www.theguardian.com/business/2010/mar/04/ineos-tax-breaks-plans-move Ineos tax deal sparks fury as firm plans move to Switzerland], theguardian.com, Thursday 4 March 2010 21.05 GMT | ||
| + | *Video: [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zG6ZZ80EKeE Jim Ratcliffe meets Stephen Sackur at BBC HARDTalk], ''YouTube - INEOSGroup'', BBC Hardtalk interview, 8 December 2016 | ||
| − | + | ====Academic reports==== | |
| − | + | *Andrew Watterson and William Dinan, [http://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/15/4/675/htm Public Health and Unconventional Oil and Gas Extraction Including Fracking: Global Lessons from a Scottish Government Review], Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15(4) | |
| − | == | ||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| Line 84: | Line 340: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | [[Category:Fracking]][[Category:Tax | + | [[Category:Fracking]][[Category:Tax avoidance]][[Category:Scotland]][[Category:Fracking Injunctions]][[Category:Chemical Industry]] |
Latest revision as of 16:09, 10 December 2019

|
This article is part of the Spinwatch Fracking Portal and project |
Ineos is a major chemicals company and a 50 per cent owner of the Grangemouth refinery in Scotland. It is part of the Ineos Group, a privately owned multinational chemicals company partly-headquartered in Rolle, Switzerland, with its registered office in Lyndhurst, United Kingdom.
British billionaire Sir Jim Ratcliffe is the founder, chairman and main shareholder, owning 60 per cent of the business. In 2018 he was ranked as Britain's wealthiest person in the annual Sunday Times Rich List after an extraordinary £15 billion rise in the value of Ineos from 2017. He was also knighted in the 2018 Queen's birthday honours list.
Once described as 'the biggest company you've never heard of', Ineos has more than 80 separate firms registered at the UK Companies House. It is the largest privately owned company in the UK. [1] In 2013 the Group's turnover was £43 billion; by 2017 this had risen to over £60 billion according to the Sunday Times Top Track 100.
Ineos has made major investments in shale gas exploration in the UK, buying up licences from BG Group and IGas Energy since 2014. It is the UK's largest shale explorer in terms of exploration licences held. In July 2016 Ineos announced it intended to accelerate UK shale gas development by lodging as many as 30 planning applications to drill test fracking wells in the north of England in early 2017. It said it hoped to begin extracting gas within 18 months.
Director Tom Crotty said he believed that once drilling started, people would 'see [fracking] is not the Frankenstein monster they thought it was'. According to the Financial Times, 'he was confident that recent changes to rules allowing ministers to intervene if local councils delay granting permission would finally lead to Ineos drilling test wells'. Until permission was granted, he admitted it 'would continue to be “difficult” to convince critics'. [2]
In addition to its shale gas acquisitions, Ineos paid £1billion for the oil and gas business of Danish firm Dong Energy in May 2017, in a buying spree that also included £200m on a North Sea oil pipeline from BP, securing it a position as one of the top 10 biggest oil and gas producers in the region.
Contents
- 1 Background
- 2 The move into shale gas
- 2.1 Views
- 2.2 Headquarters move to London
- 2.3 Buying up shale exploration licences
- 2.4 Meetings on shale gas with UK government ministers and officials
- 2.5 Revolving door
- 2.6 Lobbying against green energy taxes
- 2.7 Bullying tactics: threatens to sue the National Trust if it doesn't agree to seismic surveys
- 2.8 Hiring ex-MPs to write PR booklets
- 3 Injunction against potential protesters at its sites
- 4 Fracking in Scotland
- 5 Constituencies including INEOS licences
- 6 Legal action against Chinese companies over misuse of trade secrets
- 7 Affiliations
- 8 People
- 9 Lobbying and PR firms
- 10 Contact
- 11 Resources
- 12 Notes
Background
INEOS Group is the fourth largest chemicals company in the world measured by revenues (after BASF, Dow Chemical and LyondellBasell). It employs over 15,000 employees at 51 manufacturing plants in 11 countries. In the UK:
- INEOS Group own and run major plant at Runcorn (chlorine and caustic soda, used in many products – pharmaceuticals, synthetic fibres, bleach, water purification etc), Grangemouth in Scotland (two high energy ‘crackers’ to produce commodity chemicals used in fuels, solvents, nylon, packaging etc) and have plants based at Seal Sands, near and linked to the Wilton cluster, in the North East.
It co-owns Grangemouth with PetroChina. In July 2014 Ineos received a UK government loan guarantee to build Europe’s largest ethane storage tank at Grangemouth. The following month Ineos bought the rights to explore fracking for shale gas in a 127 square mile area around Grangemouth and the Firth of Forth.
In August 2015 Ineos Upstream was awarded a further three blocks (SK45, SK48 and SK58a) by the UK government in its first tranche of the 14th onshore licensing round.
In January 2018 Ineos announced it was creating six new oil and gas business units 'following the company’s extraordinary 2017 growth'. This has included buying up Dong Energy’s oil and gas business for $1.05bn in May 2017, and acquiring North Sea interests such as BP's Forties pipeline, making 'a top ten company in the North Sea and the biggest privately-owned exploration and production business operating in North West Europe'. As of January 2018, it had a daily production of around 95,000 boe (barrel of oil equivalent) from assets located in Norway, Denmark and the UK. [3]
The move into shale gas
Views
Back in 2013 INEOS published a lengthy article in its in-house magazine outlining its views on Europe's 'dithering' in the debate over shale gas exploration and production. It argued that action to facilitate shale gas production in the UK is imperative or chemical production in other regions, particularly the US, will gain such a competitive advantage that UK production will become uneconomic.
The firm plans to use imported US shale-derived feedstock in their chemical plants at Grangemouth. INEOS is one of the very few companies able to use shale gas as both a fuel and a feedstock.
- INEOS has decided it cannot wait, and has struck a deal with the US to bring US raw materials to its European plants to maintain a competitive global Olefins & Polymers business. From 2015 INEOS Olefins & Polymers in Norway will begin taking ‘shipments of US-derived ethane – an essential ingredient necessary to produce ethylene. [4]
INEOS warned in a report to the House of Lords EU sub-committee 'that rising energy costs threaten to undermine the ability of manufacturers in the EU to compete on the world stage'. Chemical industries that rely heavily on fossil fuels to run its plants were 'particularly at risk' it said.
- 'We are acutely vulnerable to fluctuations in energy prices,' said Tom Crotty, INEOS' group director. 'We sell our products in fiercely competitive international markets and cannot pass on costs to our customers. But we cannot afford to operate in jurisdictions with uncompetitive energy prices.'
INEOS believes that Europe 'should shield energy-hungry industries from steep price rises' while it moves towards creating affordable low-carbon energy sources.
- 'If it doesn’t, production will be forced out of Europe to more competitive locations which will mean the loss of jobs, investment and tax revenue,' he said. Decarbonisation should not mean deindustrialisation, said Tom. 'The aim must be to connect industry to green energy supplies, not push industry away,” he added. He said energy-intensive industries were not ‘sunset industries’ standing in the way of environmental improvements. 'They are actually a vital source of raw materials and innovations required to make the green economy a reality,' he said.
Headquarters move to London
In December 2016, Ineos opened a new headquarters in London, UK, saying the move reflects its increased confidence in this country. Jim Ratcliffe said they were 'planning to extract shale gas in the north of England and to grow the newly revitalised Grangemouth. We have immense confidence in Britain’s economic future – the current business climate makes siting our new headquarters in the UK an easy decision. INEOS will continue to grow both in the UK and worldwide. Britain is a good location to ensure both of these goals.'
Climate change and industry minister Nick Hurd welcomed the company's arrival with open arms, saying: 'This decision is another vote of confidence in the British economy and confirms the company’s commitment to further long-term investment and growth in this country.' [5]
Buying up shale exploration licences
2014
In August 2014 Ineos made its first move into onshore shale gas exploration in the UK, buying from BG Group a 51 per cent share of a shale licence covering 329 square km of the Midland Valley in Scotland, which includes the area around the Grangemouth refining and petrochemical complex. Dart Energy (now owned by IGas Energy) owned the other 49 per cent [6] however in March 2015 Ineos announced it was buying IGas's stake in the shale licence around the Grangemouth plant, thus giving it full ownership of the site.
2015
In March 2015 IGas agreed a deal with chemicals giant Ineos to sell it at least a 50% interest in seven of IGas’ shale gas licences in the North West along with the option to acquire a 20% interest in two further IGas licences in the East Midlands. The deal is worth £30 million in cash and a further £138 million commitment to fund a two-phase work programme to develop the sites. [7]
Ineos also pledged an extra £138m to help IGas expand its shale gas operations in the North West and East Midlands regions in England. [8]
2016
In September 2016 Ineos was reportedly planning as many as 30 applications for fracking sites in the UK within a year. 'Ineos estimates that it will be at least five years before any of its UK wells are actually producing shale gas'. [9]
2017
In March, Ineos bought up 15 shale licences from French energy company Engie for an undisclosed sum, consolidating its position as the UK's biggest shale gas explorer increasing by 10 per cent its rights to explore across 1.2m acres in the East Midlands, Yorkshire and Cheshire.
Meetings on shale gas with UK government ministers and officials
- Stephen Lovegrove, DECC Permanent Secretary met with Jim Ratcliffe on 28 June 2013 at 3 Whitehall Place. The government's briefing notes described Ratcliffe as 'very well connected and has had a number of meetings with Ministers in various Departments and with Jeremy Heywood'. A section discussing INEOS' potential activities in shale gas was redacted from the briefing note. This meeting appeared to have been suggested to Lovegrove at a 'recent Lancastrian dinner' (held in April 2013). The focus of the meeting was 'primarily... about shale gas and the importance of supporting its development' in the UK. [10]
- Duarte Figueira (Energy Development) Head of the UK Office of Unconventional Gas and Oil - with Ineos chairman Jim Ratcliffe attended the same meeting above. [10]
- Jeremy Heywood, May 2013 met with unnamed representatives of INEOS, Cuadrilla, Carillion, UKOOG, the Environment Agency and Lancashire County Council to 'discuss the potential for UK Shale Gas'. [11] [12] He met again in September 2014 with an unnamed representative of INEOS for a further 'discussion on shale gas'. [13]
- James Wharton, minister for the Northern Powerhouse met with INEOS in September 2015
Chemical industry meetings with Ministers
- Michael Fallon, in November 2013 Ineos met with the BIS minister as part of a wider group 'to discuss chemical industries'. This included Contract Chemicals, Chemical Industries Association, Huntsman, Synthomer, European Chemical Industry Council (CEFIC), Dow, Thomas Swan and Company, Croda, Verband der Chemischen Industrie e.V., Solvay, Growhow, Ineos, BASF. [14]
Attendee at UK energy minister's May 2018 shale gas roundtable
Energy minister Claire Perry hosted a roundtable with the fracking industry just hours before she gave evidence to a committee of MPs on the Conservative government's proposed changes to relax the rules on shale gas development in the UK.
A 'reconstructed' attendee list was released under the freedom of information act to North Yorkshire resident Jonathan Bales following an internal review of the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy's initial almost completely redacted FOI response. [15]
Oil and gas companies at the roundtable included:
- Aurora Energy, BP, Cuadrilla, IGas, Ineos, Third Energy and lobby group UK Onshore Oil and Gas.
- Service companies: Ground Gas Solutions, Marriott Drilling, Onshore Energy Service Group, Zetland Group.
- Investors and fund managers: Riverstone (a major partner in Cuadrilla), Kerogen (investor in IGas), Global Natural Resource Investments (formerly part of Barclays which invested in Third Energy), KKR, JP Morgan.
Other industries and organisations: Chemical Industries Association chemical company SABIC, Coalfield Regeneration Trust, Engineering Employers’ Federation, GMB. [16]
Revolving door
Secondments of senior civil servants to help develop shale gas strategy
In early 2017 Spinwatch revealed that a highly influential senior government official, Patrick Erwin had been seconded to lead Ineos' strategic push for shale in the UK since 2014.
- One stark example of the fracking industry and government interests aligning is the case of Patrick Erwin, a former top civil servant in the department of energy and climate change (DECC) and the department for communities and local government (DCLG).
- Three years ago, Erwin was seconded to work at Ineos, the petrochemical giant. His move coincided with the firm’s foray into fracking. As Ineos Upstream’s new commercial director, he was central to the development of its shale gas plans, helping it secure over one million acres in government licences to become Britain’s biggest onshore oil and gas operator.
- Erwin was Ineos' point-man for its ‘relationship with government and industry’. Documents released to Spinwatch under the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) reveal how in 2014 he organised meetings for Ineos’ billionaire owner, Jim Ratcliffe, with permanent secretary Stephen Lovegrove and other DECC top brass, ahead of the company’s final decision to enter the shale gas market.
- A regular on the shale gas conference circuit, Erwin has argued that fracking is vital for the country’s future. In a speech in summer 2015 he warned that without shale gas the UK risked becoming an environmental ‘theme park'; a strategy he called ‘massively irresponsible’.
- At the same event Erwin acknowledged the importance of talking to and 'standing up in front of communities' in potential shale gas areas. Yet less than a year later he and two other senior Ineos directors held a series of closed private meetings with parish councillors to discuss plans for Ineos license blocks in Cheshire, Derbyshire and North Yorkshire.
- Despite FOIA requests, DECC refused to publicly name Erwin as the government’s man seconded to Ineos. Erwin only declared the secondment on his LinkedIn profile after it had ended in 2016. Last month he joined Northern Powergrid as its policy and markets director. [17]
Hiring former PM and business and energy secretary special adviser
Later in 2017 Spinwatch also revealed that INEOS's lobbyists Burson Marsteller had also employed Meg Powell-Chandler, a former PM’s political aide and special adviser to UK business and energy secretary Greg Clark. Under the broken system regulating the revolving door between big business and politics, the public often has no automatic right to know about such appointments.[18]
Lobbying against green energy taxes
In April 2017 it emerged Ineos was pushing the government to use Brexit as a chance to exempt the chemicals sector entirely from climate policy costs. Documents obtained by Friends of the Earth revealed that an industry-government initiative Chemistry Growth Partnership chaired by Ineos director Tom Crotty, was lobbying to get rid of the UK’s carbon floor price ( a carbon tax on electricity generators) as part of their efforts to cut energy costs passed on to chemical companies.
The objective, as revealed in the documents, is to: 'Support appropriate policies to enable the safe exploitation of unconventional gas [shale gas], sustainable use of biofuels and optimal use of waste resources.'[19]
Bullying tactics: threatens to sue the National Trust if it doesn't agree to seismic surveys
In July 2017 Ineos said that it had been trying to get permission to carry out seismic surveys in Nottinghamshire's historic Clumber Park from the National Trust for over a year, but claimed that the Trust had refused to discuss and so Ineos was considering legal action.
- If the National Trust refuses to change its position, Ineos will have no choice but to write to the Oil and Gas Authority, asking for permission to seek a court order enforcing its rights to carry out these surveys on National Trust land,” Ineos said in a statement.
Director Tom Crotty argued that Ineos's ability to extract shale gas would be 'significantly limited' if tests could not be carried out on the Trust's land.
Ineos Shale's commercial director Lynn Calder claimed the Trust was playing politics.
- 'The National Trust is taking an overtly political position against all fossil fuels. What it fails to recognise is that shale gas is 50% cleaner than coal and 30 per cent cleaner than oil. The development of shale gas will actually reduce greenhouse gas emissions. We are developing a shale gas industry that is safe and essential for the UK and the economy. It is estimated that the industry will create tens of thousands of well-paid jobs and Ineos has pledged to give 6 permission of revenue to local people - potentially amounting to billions of pounds.” [20]
In a statement announcing the application submission, INEOS said it believes the trust has 'behaved unreasonably', adding that 'it is firmly in the national interest and a court order would back our position'. Rob Coyle, Ineos Shale's chief executive, accused the Trust of ‘failing to engage with us or the science’ and even warned that it will withhold profits from the Trust for being obstructive, if it does eventually win permission.
In January 2018 the Telegraph reported that the National Trust had sent a 'heartfelt letter' to INEOS asking it to abandon Clumber Park survey plans. Beth Dawson General manager of National Trust Clumber Park invited INEOS staff to visit the Grade-1 listed parkland, which is a designated site of special scientific interest, receives half a million visitors a year, and has a number of internationally protected species of birds. [21]
Hiring ex-MPs to write PR booklets
In December 2017 INEOS Shale controversially commissioned the former North East Derbyshire MP Natascha Engel to write an 'information 'booklet' which would 'better explain shale exploration and development' and would be distributed to locals in the areas where it was applying to drill for shale gas, such as Marsh Lane, near Eckington. Operations director Tom Pickering explained that Engel's assistance would 'give us a better insight into the needs and concerns of residents. As a former Labour MP and trade unionist, Natascha has always made the case for good jobs, as well as health and safety. At the same time, Natascha is well placed to give us a full understanding of local issues and help us to continue to be an open and inclusive organisation.'
Engel explained her rationale to carry out this work in INEOS's press release:
- I saw first-hand what the impacts are on small communities when they hear about a shale gas application near them – even when it’s only for exploratory drilling. What people want is information. They want to know how it will affect them and they want reassurance that it is safe. I hope that this booklet will provide some of those certainties.
- Most of all I hope that this will allow INEOS to work constructively with communities so that local people gain the most in terms of the jobs and apprenticeships that this industry could bring – something I have campaigned on for most of my adult life. [22]
Engel's decision was criticised by several Labour MPs. Anne Western, leader of Derbyshire Labour Group said: 'Natascha Engel’s decision to work on behalf of Ineos is shocking and disappointing. Natascha’s views on fracking are entirely her own and do not represent Labour Party policy or the views of many Labour members.'
Dennis Skinner the Labour MP for Bolsover said: 'The Labour Party is totally against fracking. Our policy, adopted at the party conference in 2016, is to ban fracking completely in the UK and to back clean technologies and renewable energy. I have been campaigning against fracking locally and in Parliament. I recently raised the matter with Theresa May at PMQs because of the water contamination at Oxcroft. Unlike Lee Rowley, who made it clear last week during a Westminster Hall debate that he doesn’t oppose fracking in principle, only in north-east Derbyshire, I am against fracking wherever it is proposed.'[23]
Injunction against potential protesters at its sites
In July 2017 Ineos Shale secured an interim High Court injunction against anti-fracking protestors[24] at a private hearing with no members of the public or press present.
Operations director Tom Pickering told the Press Association that the move by INEOS was not an attempt to quash peaceful protest but instead taken for safety reasons. He said:
- 'I have a duty of care to the employees, contractors and public at large that is in the health and safety act as written words to ensure and protect their safety and that includes a protester. As I plan for my operations, I can see all the unlawful protest that has happened. Real extreme and dangerous protest. Lorry surfing, releasing loads, blocking up a high way – all of these types of things, which are criminal acts anyway. But I think it had not been addressed with a very clear line of what is acceptable and what is not. What I want to be clear on is that we constantly respect peaceful protest. Nothing about Ineos Shale is going to stop listening to people and engaging with people.” [25]
'Draconian, anti-democratic and oppressive’
Campaigners described the move by Ineos and the courts as ‘draconian, anti-democratic and oppressive’. The high-profile group Talk Fracking, accused INEOS of trying to privatise the law, saying: ‘If this injunction is allowed to stand, it will mean that any corporation can apply for a 'pre-emptive injunction' of this nature to prevent any protest by 'persons unknown' at any site in the future, citing the INEOS injunction as a precedent. This, in effect, could shut down peaceful protest across the UK, or at least make it far more difficult to organise without running the risk of draconian punishment.’
Campaigners challenged the injunction at a court hearing in September 2017, but the judge ruled in the chemical giant's favour for it to continue. During the hearing, it emerged that INEOS had amassed thousands of pages of Facebook posts and tweets as evidence that it faced ‘a real and imminent threat’ of being targeted by unlawful protests.[26]
The company behind the Facebook surveillance was private security contractors Eclipse Strategic Security.
Campaigners take case to Court of Appeal
In January 2018 anti-fracking campaigner, Joe Corré, announced he was taking his legal case against Ineos to the Court of Appeal. Legal papers lodged with the court argue that the ‘learned judge erred in law by permitting a claim for injunctive remedies against 'Persons Unknown', as well as ‘wrongly prohibiting conduct which is lawful’. Corre's legal team also contend that the injunction breached the Court's obligations under Section 6 of the Human Rights Act and Articles 8, 10, and 11 of the European Convention on Human Rights. [26]
Victory for campaigners
In April 2019 three Court of Appeal judges finally ruled in favour of anti-fracking activists Joe Corre and Joe Boyd to overturn INEOS' sweeping and draconian injunction.
In granting the appeal, Lord Justice Longmore and two other judges ruled that INEOS' initial injunction was “too wide and insufficiently clear” and that the judge who granted the injunction had “attempted to do the impossible” - making an order that was “too wide and too uncertain”.
The judges discharged part of the original injunction relating to demonstrations in public areas and protesters combining together with the intention of damaging Ineos, which campaigners argued was having a serious effect on lawful and legitimate protest activities. According to Longmore, “The citizen’s right of protest is not to be diminished by advance fear of committal except in the clearest of cases.”
Two other aspects of the injunction remain, pending reconsideration by the high court of whether the campaigners’ right to freedom of expression as outlined in the Human Rights Act would be restricted. Reacting to the ruling INEOS boss Tom Pickering told the media: “We are talking with our legal team about our next steps, because we believe it is essential that the forces of law and order prevail. We respect peaceful protest, but we must stand up to the militants who game the legal system with intimidation and mob rule. We stand for jobs and opportunity. They stand for anarchy in the UK.”[27]
Campaigner Joe Corre said: "Today's win is a fantastic result and has restored my confidence in the British Legal system. INEOS thought they could game the British legal system by using ASBO laws designed to protect people, against the people. They can think again!" [28]
Fracking in Scotland
In 2015 Ineos launched a 'Scottish shale gas community engagement programme' to help tackle the opposition that has emerged against fracking in the region. Its campaign, dubbed 'love bombing' by campaigners, aimed to persuade people that fracking technology was safe, and how the process could bring huge economic benefits to locals.
The petrochemical company's sudden concern for the nation's economic performance was considered somewhat perplexing, given the Grangemouth controversy that had erupted just a few months earlier, when Ineos chose to keep its plant shut despite the cancellation of the planned strikes - actions that saw it accused of holding Scotland 'to ransom'.[29]
Scotland has had a moratorium on shale gas, coal bed methane and underground coal gasification since 2015. In June 2016 when the Scottish Parliament voted for a permanent ban Ineos responded by stating that the vote made little difference.
- 'The vote this evening changes very little. A process remains in place in Scotland to further assess scientific, evidence-based research before a decision is taken on fracking.
- This has important implications for the people of Scotland and its economy and should not be prejudged before it has reached its conclusion. INEOS has been clear that it believes shale gas can be extracted safely and that Scotland is losing out as the centre of excellence moves south.
- We are focused on England where we believe that shale can provide much-needed jobs, investment and energy security.' [30]
Meetings with ministers
- 28 January 2015 - First Minister Nicola Sturgeon met with INEOS chairman Jim Ratcliffe on the same day that energy minister Fergus Ewing announced a Scottish moratorium on fracking.
- 21 June 2017 - Senior Scottish ministers held private meetings with INEOS and Grangemouth executives from China five times in 13 months, reports Rob Edwards at The Ferret. Briefings released under freedom of information law show that in 2016 Nicola Sturgeon met Ineos boss Jim Ratcliffe and Chinese businessmen who are involved in helping to run the Grangemouth refinery. The Deputy First Minister John Swinney and economy secretary Keith Brown also met with Ineos managers. The purpose of the meetings has been kept secret.[31]
PR films countering anti-fracking concerns
- INEOS, Fracking facts water contamination: 'Some campaigners claim fracking leads to water contamination. That is not the case. This video explains the facts.' Published on Youtube May 2016.
- In September 2016 it was reported that '[a]s part of its campaign to win over critics, Ineos invited journalists to tour fracking sites in Pennsylvania operated by Consol, a Pittsburgh-based producer of natural gas and coal and, supposedly, an example of why fracking will be good for the UK.' [32]
First shipment of shale gas
In September 2016, a tanker carrying ethane from the US sailed up the Forth to the Ineos refinery in Grangemouth. Ineos said the shipment was the result of a £1.6billion investment in eight tankers that will form a 'virtual pipeline' for shale gas between the US and the UK and Norway. 'The Intrepid' - its smaller sibling, the INEOS Insight, was the one to dock in Forth - is one of four Dragon-class vessels that have already been delivered to Ineos. Over the next year, another four will be built and launched. [33]
Ineos claims the gas will replace dwindling North Sea supplies, and secure the future of Grangemouth’s 1300 workforce, and a further 9000 Scottish jobs.
When the shipment arrived, many politicians and environmental groups criticised the gas, fearing it will be a first step on the road to allowing fracking in Scotland. Mark Ruskell MSP, the Scottish Greens' climate, energy and environment spokesman, said:
- 'As well as shale gas, the so-called 'dragon' fleet of ships docking in Scotland will also bring with them a renewed campaign by Ineos for fracking to be given the go ahead. The Scottish Government must legislate for an outright ban on fracking because its vague 'moratorium' policy is clearly giving hope to fossil fuel giants intent on digging up Scotland.' [34]
PR Junket for journos to greet the US shale gas supertanker arrival
INEOS wined and dined journalists and paid for their 4-star hotel overnight stays in Edinburgh plus return flights to the city, as part of a PR junket to promote the arrival of its super gas tankers from the US. Scottish investigative site The Ferret reported that INEOS was due to host a dinner at the Wedgwood restaurant, with breakfast the following morning on a boat on the Firth of Forth ahead of meeting the gas tanker INEOS Insight. Longstanding INEOS PR company Media Zoo organised the junket. The event received extensive press coverage across the UK. [35]
Responses to the Scottish Government report and moratorium
On the Scottish Government's decision to impose both a report and moratorium on fracking, Ratcliffe said: 'We have no objection to people evaluating safety and environmental issues, I think that’s all very fair and proper. But it probably would have been quite sensible to let us at least do the exploration phase in Scotland.' [36]
One of the biggest fears of the Scottish government regarding shale gas is the lack of regulation shown in the US. In September 2016, Ineos insisted that fracking in the UK will be different than in the US. It argued that technology has come a long way over the past decade. Also, as the US fracking industry has matured, lessons were learned, making it easier to replicate best practices on fracking sites in the UK. To ease the inconvenience of light, noise and traffic during drilling, Ineos also promised to give 6% of its profits to the UK communities where it will frack. [9]
In 2018, Ineos took Scottish ministers to court for introducing what it deemed was an 'effective ban' on fracking in the form of the moratorium. The court dismissed Ineos' multi-million damages claim however concluded that the Scottish Government had not banned fracking.
APPG Debate on fracking in Scotland
In a debate hosted by the All Party Parliamentary Group on Unconventional Oil and Gas (APPGUOG) in December 2016, Stephen Tindale, now a consultant to INEOS Shale, defended the idea of fracking in Scotland. He argued that '[s]hale is a necessary part of decarbonisation' as the demand for gas-based sources of heating will remain high for several decades. Tindale also argued that, while shale gas extraction did not have a public license now, it did have a human rights element to it as it would mean less dependency on imports from states who do not respect the human rights of their people. He responded to the argument that fracking destroyed jobs in other sectors such as renewables and conventional oil and gas by blaming the government instead for its erratic policies on renewables.
On the question of whether shale gas extraction is beneficial to the economy, Tindale said:
- 'Nobody knows because the geology of the UK is very different from the US so it needs to be tested. Is that a waste of money? It might be. The question then is whose money is it? Is it public money? No. [...] [W]e shouldn’t give public money to it but we should be prepared to allow them [the companies] to proceed [investments] if they have their own money. [37]
Ineos PEDL licence extended in 2019 for the second time
On 1 July 2019 the Scottish Government renewed an onshore petroleum exploration and development licence PEDL 162, which is 80 per cent owned by Ineos and permits fracking and other underground gas extraction technologies. The licence covers 400sq km to the south and west of Falkirk, and was extended for another year. It had already been extended for one year from July 2018. Reach Coal Seam Gas owns the other 20 per cent.
According to the Ferret:
- PEDL 162 was originally granted by the Westminster government to a firm called Reach Coal Seam Gas in 2008. Ineos bought four-fifths of the licence in 2014, and responsibility for licensing was devolved to Holyrood in February 2018. [38]
Reach Coal Seam Gas's own press release in 2014 announcing it had farmed out 80 per cent of the licence to Ineos states that it had previously 'conducted extensive geological studies which have shown PEDL162 may contain large amounts of producible hydrocarbons'. [39]
Campaign groups and communities were dismayed by the announcement of the license extension reports The Ferret. However Scottish energy minister Paul Wheelhouse argued in a letter released 28 June that: “It would have been a dereliction of our responsibility as a competent licensing authority not to consider the request for an extension, taking into account all the relevant factors.”
The decision followed a request submitted by the licensees said Wheelhouse, and a second round of extended consultations on the environmental and business impact of the government’s opposition to fracking which concluded 25 June 2019. The extension to PEDL 162 would give time for the policymaking process to conclude and for licensees to consider their position, Wheelhouse argued. [40]
Constituencies including INEOS licences
- Altrincham and Sale West - Graham Brady
- Amber Valley - Nigel Mills, MP Conservative
- Ashfield Co - Gloria de Piero
- Barnsley Central - Dan Jarvis
- Barnsley East – Michael Dugher
- Bassetlaw - John Mann
- Bolsover - Dennis Skinner
- Chesterfield - Toby Perkins
- Congleton - Fiona Bruce, MP Conservative
- Derbyshire Dales - Patrick McLoughlin, MP Conservative
- East Yorkshire - Greg Knight
- Eddisbury - Antoinette Sandbach
- Halton - Derek Twigg
- Macclesfield - David Rutley
- Mansfield - Alan Meale
- NE Derbyshire - Natascha Engel (Labour) until June 2017, replaced by Conservative Lee Rowley. Engel was later contracted by Ineos to write a report on shale gas development. She also was appointed the UK's first ever shale gas commissioner in October 2018, but had resigned by April 2019 over the government's refusal to revisit the regulations over seismic levels during shale gas operations.
- Newark - Robert Jenrick
- Penistone and Stockbridge - Angela Smith, MP Conservative
- Richmond (Yorks) - Rishi Sunak
- Rother Valley - Kevin Barron - includes the Harthill and Woodsetts sites. By June 2018 Hartill had received permission, and a revised Woodsetts application had been re-submitted.
- Rotherham - Sarah Champion
- Scarborough and Whitby – Robert Goodwill, MP Conservative
- Sheffield Central - Paul Blomfield
- Sheffield Hallam - Nick Clegg
- Sheffield SE - Clive Betts
- Sheffield, Brightside and Hillsborough - Gill Furniss
- Sheffield, Heeley - Louise Hay
- Sherwood - Mark Spencer
- Tatton - George Osborne, MP Conservative
- Thirsk and Malton - Kevin Hollinrake, MP Conservative
- Warrington South - David Mowat
- Weaver Vale - Graham Evans
- Wentworth and Dearne - John Healey
- York Central - Rachael Maskell
- York Outer - Julian Sturdy
Legal action against Chinese companies over misuse of trade secrets
In March 2014 Ineos announced it was taking legal action against a number of Sinopec and Sinopec subsidiaries (SNEC, Anqing and others) for breach of contract and/or misuse of trade secrets.
- INEOS says that Sinopec Ningbo Engineering Company has broken a long established technology agreement which, together with trade secret misuse by other Sinopec companies, has enabled development of a series of new world-scale Acrylonitrile plants without INEOS agreement or consent. INEOS, which has otherwise excellent relationships with Sinopec and with China, has no choice other than to protect its intellectual property. INEOS fears that these breaches of rights will cause major harm to its Acrylonitrile business which generates up to $500m per annum of profit and has a replacement value of $3 billion. It supports around 5,000 direct and indirect jobs in the USA and Europe. [41]
Affiliations
- All Party Parliamentary Group on Unconventional Oil and Gas - Ineos was an associate member, as well as a member of the 'independent advisory panel' of this controversial APPG. Its first contribution was £10,000, which was registered in June 2013. The APPG ceased four years later, following the 2017 general election. It was administered by two big lobbying agencies during its operation: Edelman and Hill and Knowlton.
- Parliamentary and Scientific Committee (an Associate Parliamentary Group)
People
- Jim Ratcliffe - founder and chairman
- Tom Crotty - INEOS group and external affairs director
- Tom Pickering - chief financial officer
- Andrew McLachlan - senior account director
- Peter Rose - business development director, speaker at ShaleWorld UK conference
- Gary Haywood, CEO of INEOS Upstream and in charge of leading the company’s fracking plans
- John McNally, chief executive of Ineos’s UK petrochemicals arm
- David East, communications manager
Former executives
- Patrick Erwin, commercial director of Ineos Upstream, leading on commercial strategy, developing partnerships and on asset purchase - led the economics and work programme parts of for INEOS’s application to the 14th Onshore Licensing Round. Seconded from central government 2013-May 2016, then on staff until December 2016 before leaving to join Northern Powergrid.
- Calum MacLean - a founder member of INEOS in 1998 and chairman O&P Europe and chief executive officer O&P Europe (UK) since 2011. He left to join rival chemical company Synthomer in January 2015. Several months later Ineos COO Steve Bennett also joined the company. [42]
Lobbying and PR firms
External
{{#ev:youtube|https://youtu.be/toTLr2yIJ5E%7C450%7Cright%7CWatch 'Meet the Frackers: a Spinwatch lobbying tour' to find out more about the lobbyists INEOS hires to help it push fracking in the UK}} *Burson-Marsteller (B-M) took over the Ineos account in July 2014 from Portcullis Public Affairs who had retained it for several years. Freedom of information requests reveal that B-M has set up meetings with UK government ministers for INEOS. In 2017 B-M hired Meg Powell-Chandler, a former special adviser to business and energy minister Greg Clark and former prime minister David Cameron. [43] In June 2018 Trade industry magazine PRWeek reported that B-M was no longer handling Ineos's account.
- PPS Group provides public affairs advice to Ineos Enterprises Ltd (2014-2015)
- Media Zoo’s UK media relations and reputation management brief includes communicating with trade organisations and governments in the US and Germany, which are key markets for Ineos. [44] Creative director Mark Killick works on the Ineos account. [45] along with Andrew McLachlan and Hannah Brandstaetter. Media Zoo has also facilitated press trips from the UK to view the company's operations in the US
- Edelman [46]
Internal
- Richard Longden (INEOS)
Contact
- Website: http://www.ineos.com/
- Twitter: @INEOS_Upstream
- London address: 38 Hans Cres, London SW1X 0LZ
Resources
On Powerbase and Spinwatch
See: Fracking lobbying firms See: Fracking Spads
- Melissa Jones and Andy Rowell, Access all areas: Westminster's (vast) fracking lobby exposed, 29 April 2015.
- Video: Meet the Frackers: a Spinwatch lobbying tour, Spinwatch | YouTube, 16 January 2017.
- Andy Rowell, SLAPPS and ‘aggressive cold calling’: How INEOS is selling shale, Spinwatch August 2017
- Melissa Jones, Time to fix the revolving door rules for special advisers, Spinwatch, 17 October 2017
- Andy Rowell, Exclusive: Fight against INEOS' ‘draconian’ injunction goes to the Court of Appeal. Spinwatch, 19 January 2018
Ineos
Ineos Public relations video series
- Video: Why do we need fracking?, YouTube - INEOS Group, 13 May 2016
- Video: Fracking facts what is fracking, YouTube - INEOS Group, 13 May 2016
- Video: Fracking facts water contamination, YouTube - INEOS Group, 13 May 2016
- Video: Fracking facts earthquakes, YouTube - INEOS Group, 13 May 2016
- Video: Fracking facts air quality, YouTube - INEOS Group, 13 May 2016
- Video: Fracking facts chemicals, YouTube - INEOSGroup, 13 May 2016
- INEOS YouTube channel, YouTube - INEOS Group
PR supplements
- Ineos, File:Ineos-fracking-supplement-2017.pdf, advertising feature pull-out, this version published in the Derbyshire Times,28 January 2017 [pdf download]
Freedom of information requests
- Letter regarding FOI request on INEOS introductory meeting with DECC Permanent Secretary June 2013, Office of Unconventional Gas and Oil (OUGO), dated 27 January 2014, acc 5 May 2014
- Emails, Email exchanges of 30th June between Ineos and DECC Officials. Briefing material for 28th June Meeting 3. Email exchanges between Ineos and DECC Officials
News articles and video
- Letter to the Editor Ineos, tax and China, The Guardian, Monday 21 October 2013 21.00 BST
- US shale gas plan to make Grangemouth profitable, The Telegraph, 2 September 2013
- Simon Goodley, firm Ineos accused of ‘bribes and bulldozers’ approach to fracking, The Guardian, 28 September 2014
- Nick Mathiason, Ineos tax deal sparks fury as firm plans move to Switzerland, theguardian.com, Thursday 4 March 2010 21.05 GMT
- Video: Jim Ratcliffe meets Stephen Sackur at BBC HARDTalk, YouTube - INEOSGroup, BBC Hardtalk interview, 8 December 2016
Academic reports
- Andrew Watterson and William Dinan, Public Health and Unconventional Oil and Gas Extraction Including Fracking: Global Lessons from a Scottish Government Review, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15(4)
Notes
- ↑ Nick Mathiason, Ineos tax deal sparks fury as firm plans move to Switzerland, theguardian.com, Thursday 4 March 2010 21.05 GMT
- ↑ Peggy Hollinger, Industry Editor Ineos targets British test wells to kick-start shale gas market, Financial Times, 17 July 2016, accessed same day
- ↑ Ineos, INEOS launches six new oil and gas businesses, Ineos website, 15 January 2018, accessed 31 January 2018
- ↑ Inch Magazine Material Gain, 2013
- ↑ Ineos opens new base in London, Energy Voice, 6 December 2016, accessed 22 December 2016.
- ↑ Ineos, INEOS moves into UK shale gas exploration, Press release dated 18 August 2014
- ↑ INEOS to acquire significant share of key IGas North-West shale gas assets, Ineos press release, 10 March 2015, accessed same day
- ↑ IGas signs £30m shale gas deal with Ineos to expand, BBC News, 10 March 2015, accessed same day
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Jana Kasperkevic, In Ohio, frackers are drilling. Soon Ineos will be doing the same in Britain, The Guardian, 17 September 2016. Accessed 22 December 2016.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Email exchanges of 30th June between Ineos and DECC Officials. Briefing material for 28th June Meeting 3. Email exchanges between Ineos and DECC Officials, see page 7 of 17 for this reference.
- ↑ Damian Carrington, Emails reveal UK helped shale gas industry manage fracking opposition, The Guardian, 17 January 2014, accessed 5 January 2017.
- ↑ Jeremy Heywood's released external meetings April to June 2013
- ↑ Jeremy Heywood's released external meetings Q2 2014-2015
- ↑ Transparency data BIS ministerial meetings: October to December 2013, Published May 2014, acc 6 November 2013
- ↑ What do they Know?, Shale Gas Round Table: internal review of Freedom of Information request to Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy, 24 July 2018
- ↑ Ruth Hayhurst, What government told the shale gas industry about success, regulation, jobs and support, Drill or Drop, 22 October 2018, accessed same day.
- ↑ Melissa Jones, Meet the Frackers’: a Spinwatch lobbying tour , Spinwatch, 15 January 2017
- ↑ Melissa Jones, Time to fix the revolving door rules for special advisers, Spinwatch, 17 October 2017
- ↑ Adam Vaughan, Fracking firm Ineos leads industry lobbying to avoid green tax, The Guardian, 3 April 2017
- ↑ Alan Jones, Ineos threatens to sue National Trust so it can carry out fracking survey on its land, Independent, 20 July 2017, accessed 21 August 2017
- ↑ Sarah Knapton, National Trust sends heartfelt letter to fracking company asking it to abandon Clumber Park survey plans, Telegraph.co.uk, 7 January 2018
- ↑ INEOS Shale commission former MP Natascha Engel, INEOS Shale, 1 December 2017, accessed Dec 2017, and 7 Jan 2018
- ↑ Decision by former MP to link up with fracking firm criticised, Derbyshire Times, 6 December 2017
- ↑ Upstream Limited and others v Persons Unknown Approved Note of Judgment of Mr Justice Morgan dated 28 July 2017
- ↑ Press Association, Brexit vote sparked ‘shift in tone’ on fracking, says Ineos boss, Energy Voice, 27 August 2017, accessed 28 August 2017
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Andy Rowell, Exclusive: Fight against INEOS' ‘draconian’ injunction goes to the Court of Appeal, Spinwatch, 19 January 2018
- ↑ Rob Evans, [https://www.theguardian.com/law/2019/apr/03/protesters-hail-legal-victory-over-fracking-firms-injunction Protesters hail legal victory over fracking firm's injunction', The Guardian, 3 April 2019, accessed same day.
- ↑ Ruth Hayhurst, Breaking: Anti-fracking campaigners win appeal against Ineos protest injunction, DrillorDrop, 3 April 2019.
- ↑ Holyrood Exposed: A Guide to Lobbying in Scotland, squarespace.com, 12 October 2015, accessed 12 October 2015
- ↑ INEOS Upstream, Twitter
- ↑ Rob Edwards, Revealed: Scottish ministers’ meetings with fracking firm The Ferret, June 21, 2017
- ↑ Jana Kasperkevic, In Ohio, frackers are drilling. Soon Ineos will be doing the same in Britain, The Guardian, 17 September 2016. Accessed 22 December 2016.
- ↑ Shale tsunami: the virtual pipeline funnelling oil to Europe's shores, Offshore Technology, 19 December 2016, accessed 22 December 2016.
- ↑ First shipment of shale gas from US arrives in Grangemouth, met by angry environmentalists, Daily Record, 27 September 2016. Accessed 22 December 2016.
- ↑ Ferret Journalists, INEOS PR plan to greet fracking boat, The Ferret, September 26, 2016
- ↑ First shipment of US shale gas to arrive in Scotland as fracking debate continues, Daily Record, 26 September 2016. Accessed 22 December 2016.
- ↑ [ http://www.theenergycollective.com/energy-post/2394513/fracking-gang-plank-to-climate-chaos-or-necessary-part-of-decarbonization Fracking: ‘Gang Plank to Climate Chaos’ or ‘Necessary Part of Decarbonization’?], Energy Collective, December 7, 2016, accessed December 22, 2016.
- ↑ Rob Edwards, [https://theferret.scot/pedl-162-ineos-fracking-licence-renewed/ Scottish Government move to renew Ineos fracking licence ‘disappointing’], The Ferret, 1 July 2019, accessed same day
- ↑ Reach CSG, Press Releasee, 13 October 2014, accessed 1 July 2019
- ↑ Rob Edwards, [https://theferret.scot/pedl-162-ineos-fracking-licence-renewed/ Scottish Government move to renew Ineos fracking licence ‘disappointing’], The Ferret, 1 July 2019, accessed same day
- ↑ INEOS announces legal action against Sinopec and Sinopec subsidiaries, 21 March 2014, acc 5 May 2014
- ↑ Joanna Burke, Ineos boss to sue former right-hand man for hiring 'in breach of terms', The Independent, 2 April 2015
- ↑ *Melissa Jones, Time to fix the revolving door rules for special advisers, Spinwatch, 17 October 2017
- ↑ Glen Munro, Grangemouth owner Ineos awards corporate work to Media Zoo, prweek.com, 21 January 2014
- ↑ Mark Killick, The comms battle for Grangemouth, PRWeek, January 07, 2014, acc 20 August 2014
- ↑ PRCA Public Affairs Register: Consultancies – March to May 2013