World Zionist Organization

The World Zionist Organisation is an umbrella organisation for the Zionist movement aimed at the creation and maintenance of a Jewish state in Palestine. It was formed in 1897 by Theodor Herzl as the Zionist Organization (renamed "World Zionist Organization" in 1960) and has held the Zionist congress every two years since. It is one of four intertwined organisations that form the Israeli National Institutions, all of which are based in the same building in Jerusalem.
History
The first Zionist congress convened by Herzl in 1897 is often seen as the founding of the Zionist movement. Herzl had articulated his desire for the creation of a Jewish state in his 1896 book Der Judenstaat and the congress, held in Basle, aimed to express this institutionally.
Presidents of the World Zionist Organisation
This table lists the presidents of the WZO and their term of office.
| Name | years |
|---|---|
| Yaakov Hagoel | 2020-present |
| Avraham Duvdevani | 2005-2020 |
| Zeev Bielski | 2005-2009 |
| Sallai Meridor | 1999-2005 |
| Avraham Burg | 1995-1999 |
| Yehiel Leket | 1994-1995 |
| Simcha Dinitz | 1987-1994 |
| Aryeh Dolchin | 1978–1987 |
| Yosef Almogi | 1976-1978 |
| Aryeh Dolchin | 1975-1976 |
| Pinhas Sapir | 1975-1975 |
| Aryeh Dolchin | 1973-1975 |
| Louis Arie Pincus | 1972-1973 |
| Ehud Avriel | 1968-1972 |
| Nahum Goldmann | 1956-1968 |
| David Ben-Gurion | 1956-1946 |
| Chaim Weizmann | 1935-1946 |
| Nahum Sokolow | 1931-1935 |
| Chaim Weizmann | 1921-1931 |
| Otto Warburg | 1911-1921 |
| David Wolffsohn | 1905–1911 |
| Binyamin Ze'ev Herzl | 1897–1904 |
Funding settlement construction
In 2012 the WZO's Settlement Division "financed NIS 400,000 worth of infrastructure work in the West Bank outpost of Negohot, even though the work was carried out without building permits".[1] Whereas all Israeli settlements are illegal under international law, "outposts" are also illegal under Israeli law. As Ha'aretz reports, the Settlement Division has form when it comes to funding their construction:
- "A report on unauthorized West Bank outposts that the state commissioned from attorney Talia Sasson in 2005 found serious flaws in the Settlement Division’s conduct. Inter alia, it found that the division regularly funded illegal construction in many locales.
- In response to Sasson’s report, then-Attorney General Menachem Mazuz issued orders barring the use of public funds for illegal construction. Those orders applied to all public bodies and explicitly defined legal construction as construction carried out in accordance with a valid master plan.
- In addition, the Finance Ministry assigned an accountant to the Settlement Division to monitor its conduct. The accountant is subordinate to the treasury’s accountant general, and his task is to ensure that the division’s financial conduct complies with Israeli law.
- Since then, violations of the rules like what happened at Negohot have become rare."[1]
In response to the Ha'aretz report the Settlement Division acknowledged funding construction in Negohot, but denied that said construction was illegal.[1]
The budget of the WZO's Settlement Division comes from the Israeli state, and has grown every year. In 2012 it was supposed to be NIS 60 million, but rose to NIS 272 million by the year's end.[1]
Members and affiliates
Affiliations
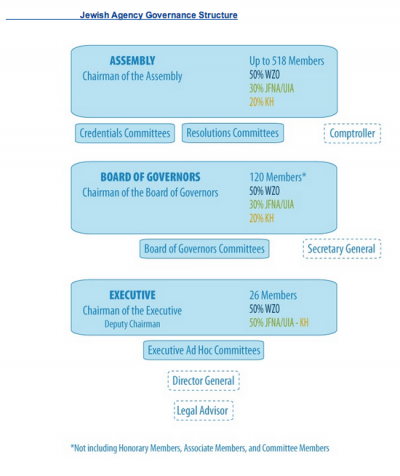
The World Zionist Organization is allocated 50% of the votes on the governing bodies of the Jewish Agency. The JFNA/UIA has 30% of the votes and Keren Hayesod (which does not operate in the US, but covers the rest of the world) is allocated 20%.[2]
Members - Zionist Federations
There are thirty two members from 31 countries (there are two in the UK).
16 in Western Europe, 8 in Latin America, 2 in North America, Australasia, Eastern Europe and one in Africa and in Asia.
Latin America
Organización Sionista Argentina | Consejo Sionista De Mexico A.C. | Organizacion Sionista de Panama | Federacion Sionista del Peru | Federacion Sionista de Chile | Asoc. Centro Israelita Sionista de Costa Rica| Organizacion Sionista del Uruguay | | Federacion Sionista de Venezuela
Australasia
Zionist Federation of Australia | Zionist Federation of New Zealand (ZFNZ) |
Western Europe
Zionistische Federation in Oesterreich | Zionistische Federation in Bulgaria | | Zionistische Federation in Belgium | Romanian Zionist Association (RZA) | Federación de Comunidades Judías de España | Zionist Federation of Denmark | Zionist Federation of Sweden | Fédération des Organisations Sionistes de France (FOSF) | Swiss Zionist Federation | Zionistische Federation in Deutschland (ZOD) | Zionist Federation of Greece | | Zionist Federation of Holland | Zionist Federation of Great Britain & Ireland | Mizrachi UK | Zionist Federation of Hungary - Magyarországi Cionista Szövetség | Zionist Federation of Italy
North America
Canadian Zionist Federation (CZF) | American Zionist Movement (AZM) |
Eastern Europe
Zionist Federation of Russia (MORIA) | Zionist Organization of Ukraine
Africa
South African Zionist Federation (SAZF) |
Asia
Zionist Federation of India [3]
World Unions
Circa 2014
Arzenu | World Herut | World Israel Beytenu | World Likud | World Meretz | World Mizrachi | World Avoda | World Kadima | Mercaz Olami[4] | World Confederation of United Zionists[5]
Circa 2024
World Likud | Shas Olami | Eretz Hakodesh | Mizrachi | World Israel Beytenu | World Herut | Lavi Olami | Arzenu | Mercaz Olami | World Avoda | Kachol Lavan | Yesh Atid | World Union of Meretz | Tnuat Hamerkaz Haliberalit Hanoar Hatzioni | World Confederation of United Zionists[6]
Affiliated organisations
World Na'amat | World Sephardi Federation | World Masorti | World Emunah | World Maccabi | Hadassah | Women's Interational Zionist Organization | World Union for Progressive Judaism | B'nai B'rith International | World Union of Jewish Students | World Organization of Orthodox Communities and Synagogues in Israel and Diaspora[7]
Youth Movements
Hashomer Hatzair | Hanoar Hatzioni | Tzameret | Hamahanot Ho'olim | Haihud Hahaklai | Ariel | Betar | National Youth/Noar Leumi | The General Federation Of Working And Studying Youth/HaNoar HaOved VeHaLomed (NOAL) | Tzofim | World Bnei Akiva | Maccabi Hatzair | Ezra | Habonim Dror | Netzer Olami[8]
Young Adult Movements
PZC | Magshimei Tora VeAvode | Bana | Tagar | Tamar | Maccabi | Atid | Marom | Magshimei Herut | Kidma | Kidma Anilevich [9]
Partners
Jewish Agency for Israel | Keren Hayesod | Jewish National Fund [10]
See also
- West European Public Relations Group for Information on Behalf of Israel | Zionist Organization of America | The Duties of the Individual Zionist | World Zionist Congress
Further reading
- Geographic Israel World Zionist Organization and the Jewish Agency Based on the following sources: The Library of Congress Country Studies; CIA World Factbook
- Jewish Virtual Library
- Wikipedia World Zionist Organization
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Chaim Levinson, World Zionist Organization funneled NIS 400,000 into infrastructure work at illegal West Bank outpost, Ha'aretz, 19 August 2013
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Jewish Agency Jewish Agency Governance Structure. Accessed 16 February 2014.
- ↑ WZO Zionist federations. Accessed 12 February 2014.
- ↑ WZO World Unions. Accessed 15 February 2014.
- ↑ WZO The Zionist World Unions.
- ↑ https://www.wzo.org.il/page/partners/factions/en
- ↑ WZO Affiliated Zionist Organizations. Accessed 15 February 2014.
- ↑ WZO Youth Movements. \Retrieved from the Internet Archive onf 11 March 2018.
- ↑ WZO Young Adults Movements, retrieved from the Internat Archive of 7 July 2022.
- ↑ WZO Partners. Accessed 15 February 2014.