Difference between revisions of "Islamist-Islamism"
(→Gilles Kepel and Olivier Roy) |
(→Gilles Kepel and Olivier Roy) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
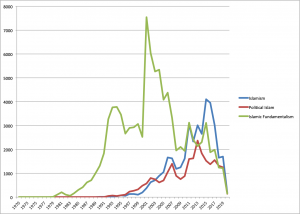
[[File:Islamism-Anglophone press-1970-2020.png|thumb|right|300px|'Islamism', 'political Islam' and Islamic fundamentalism in the Anglophone press 1970-2020]] | [[File:Islamism-Anglophone press-1970-2020.png|thumb|right|300px|'Islamism', 'political Islam' and Islamic fundamentalism in the Anglophone press 1970-2020]] | ||
| − | [[Gilles Kepel]] and [[Olivier Roy]], both French academics helped to give the term Islamist currency in early adoptions of the term. | + | [[Gilles Kepel]] and [[Olivier Roy]], both French academics helped to give the term Islamist currency in early adoptions of the term. Kepel wrote a piece in a French journal in 1984 focused on Egypt.<ref>KEPEL, G. (1984, January). CONTEMPORARY EGYPT-THE ISLAMIST MOVEMENT AND THE LEARNED TRADITION. In ANNALES-ECONOMIES SOCIETES CIVILISATIONS (Vol. 39, No. 4, pp. 667-680). 54 BD RASPAIL, 75006 PARIS, FRANCE: LIBRAIRIE ARMAND COLIN. |
| + | </ref> Meanwhile Roy wrote three early pieces in 1983/4, all focused on the Afghan conflict.<ref>Roy, O. (1983). Sufism in the Afghan resistance. ''[[Central Asian Survey]]'', 2(4), 61-79.; Roy, O. (1984). The origins of the Islamist movement in Afghanistan. ''[[Central Asian Survey]]'', 3(2), 117-127.; | ||
| + | Roy, O. (1984). Islam in the afghan resistance. ''[[Religion in Communist Lands]]'', 12(1), 55-68.</ref> | ||
Kepel and Roy eventually fell out over their differing views.<ref>Adam Nossiter [https://www.nytimes.com/2016/07/13/world/europe/france-radical-islam.html ‘That Ignoramus’: 2 French Scholars of Radical Islam Turn Bitter Rivals] ''New York Times'' 12 July 2016.</ref> | Kepel and Roy eventually fell out over their differing views.<ref>Adam Nossiter [https://www.nytimes.com/2016/07/13/world/europe/france-radical-islam.html ‘That Ignoramus’: 2 French Scholars of Radical Islam Turn Bitter Rivals] ''New York Times'' 12 July 2016.</ref> | ||
| − | |||
==Central Asian Survey== | ==Central Asian Survey== | ||
Revision as of 13:09, 18 February 2020
Islamism (and the associated Islamist) are terms that are used very widely in contemporary discourse.
Contents
History of usage
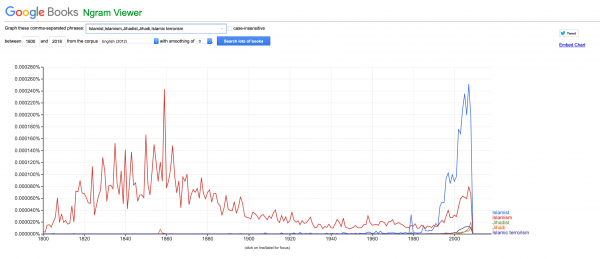
The term Islamism historically referred to adherents of Islam. It was a term used widely in English from as early as 1800, peaking in books published in English around 1860 and declining to residual use by the turn of the century. Its occurrence only picked up, as the Google Ngram image shows, but this time in a mostly new sense, at the end of the 1980s.
What caused the reinvention and reinterpretation of the term Islamism (and around the same time, the coining of a new term to go with it - Islamist)?
Bernard Lewis
On of the earliest articles of note was by Bernard Lewis a 'renowned British-American historian of Islam and the Middle East. A former British intelligence officer, Foreign Office staffer, and Princeton University professor.'[1]
In January 1976 he published a piece in the Zionist/Neoconservative magazine Commentary, which at that stage was still published by the American Jewish Committee. Titled 'The return of Islam' it raised the spectre of 'new forms of pan-Islamic activity.'[2] It sets out to insist that the problem with Islam is that it is a religion. Thus he chides the West for not understanding that Muslims are not like us. 'We are prepared' he states 'to allow religiously defined conflicts to accredited eccentrics like the Northern Irish, but to admit that an entire civilization can have religion as its primary loyalty is too much.'[2]
The phrase 'pan-Islamism' was used nine times in the piece in an account that proposed that the problem with Muslims in politics is that they take their religion too seriously. Bernard Lewis 'was not a regular rogue. He was instrumental in causing enormous suffering and much bloodshed in this world. He was a notorious Islamophobe who spent a long life studying Islam in order to demonise Muslims and mobilise the mighty military of what he called "the West" against them.'[3]
Martin Kramer

Four years later Martin Kramer - both student and friend of Lewis - introduced the term 'Political Islam':
- Terminology for the phenomena characterized as Political Islam varies among scholars. The first scholar to introduce the term Political Islam was Martin Kramer in 1980. Some scholars use the term Islamism for the same set of phenomena, or use the two terms interchangeably. Dekmejian 1980 was among the first to place the politicization of Islam in the context of the failures of secular governments, although he uses the terms Islamism and fundamentalism (rather than Political Islam) interchangeably. Dekmejian 1995, still using fundamentalism and Islamism, is an influential treatment of Political Islam as increasingly mainstream and moderate. Some scholars, using descriptive terms such as conservative, progressive, militant, radical, or jihadist, distinguish among ideological strains of Political Islam.[4]
Kramer's book was published by Sage but in a series called the 'Washington Papers'. This was edited by Walter Laqueur the historian, journalist, propagandist and 'terror expert' who was at the time attached to the Georgetown University think tank the Center for Strategic and International Studies. The book only used the term 'Islamism' on four occasions, in each case with the prefix 'Pan' as in 'Pan-Islamism'. the idea that Muslims involved in politics might all be part of the same phenomenon seems to have been an intoxicating one.
Gilles Kepel and Olivier Roy
Gilles Kepel and Olivier Roy, both French academics helped to give the term Islamist currency in early adoptions of the term. Kepel wrote a piece in a French journal in 1984 focused on Egypt.[5] Meanwhile Roy wrote three early pieces in 1983/4, all focused on the Afghan conflict.[6] Kepel and Roy eventually fell out over their differing views.[7]
Central Asian Survey
Resources
- Dekmejian, R. Hrair. “The Anatomy of Islamic Revival: Legitimacy Crisis, Ethnic Conflict and the Search for Islamic Alternatives.” The Middle East Journal 34, no. 1 (1980): 1–12.
- Krieg, Andreas Laying the ‘Islamist’ bogeyman to rest Lobelog, October 10, 2019
- Lewis, Bernard, “The Return of Islam.” Commentary 61, no. 1 (1976): 39–49.
- Sayyid, Salman, (2015). A fundamental fear: Eurocentrism and the emergence of Islamism. Zed Books Ltd.
- Scardino, Albert, 1-0 in the propaganda war The guardian, 4 February 2005.
- Smith, Blake, Why We Say ‘Islamism’ and Why We Should Stop, Quillette. 11 February 2018
Notes
- ↑ Militarist Monitor, Bernard Lewis, last updated: September 17, 2018.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Lewis, Bernard, “The Return of Islam.” Commentary 61, no. 1 (1976): 39–49.
- ↑ Hamid Dabashi Alas, poor Bernard Lewis, a fellow of infinite jest, Al Jazeera, 28 May 2018.
- ↑ John O. Voll, Tamara Sonn Political Islam Oxford Bibliographies, LAST REVIEWED: 29 SEPTEMBER 2014, LAST MODIFIED: 14 DECEMBER 2009 DOI: 10.1093/OBO/9780195390155-0063.
- ↑ KEPEL, G. (1984, January). CONTEMPORARY EGYPT-THE ISLAMIST MOVEMENT AND THE LEARNED TRADITION. In ANNALES-ECONOMIES SOCIETES CIVILISATIONS (Vol. 39, No. 4, pp. 667-680). 54 BD RASPAIL, 75006 PARIS, FRANCE: LIBRAIRIE ARMAND COLIN.
- ↑ Roy, O. (1983). Sufism in the Afghan resistance. Central Asian Survey, 2(4), 61-79.; Roy, O. (1984). The origins of the Islamist movement in Afghanistan. Central Asian Survey, 3(2), 117-127.; Roy, O. (1984). Islam in the afghan resistance. Religion in Communist Lands, 12(1), 55-68.
- ↑ Adam Nossiter ‘That Ignoramus’: 2 French Scholars of Radical Islam Turn Bitter Rivals New York Times 12 July 2016.