Erio Barale-Thomas
Erio Barale-Thomas is a toxicologist. He is president of the Administrative Council of the Société Française de Pathologie Toxicologique (SFPT, French Society of Toxicological Pathology). Barale-Thomas describes the SFPT as "a non governmental/non profit organization formed by veterinarians, physicians, pharmacists and biologists specialized in veterinary and toxicologic pathology".[1]
It was as spokesperson for this nonprofit organisation that he wrote a letter to the editor of the journal Food and Chemical Toxicology, condemning "weaknesses" and "deficiencies" in the paper of Prof G. E. Séralini (2012), published in September 2012 in the same journal.[2]
Séralini's study had found severe organ damage, increased tumours and premature mortality in rats fed the commercialised genetically modified (GM) maize NK603, developed by Monsanto, and its associated herbicide Roundup.[3]
In his letter, Barale-Thomas takes Seralini to task for failure to declare a conflict of interest in his paper, namely the fact that Seralini is president of CRIIGEN, the independent research group based in France, which contributed funding to the research - a fact that was declared in the paper.
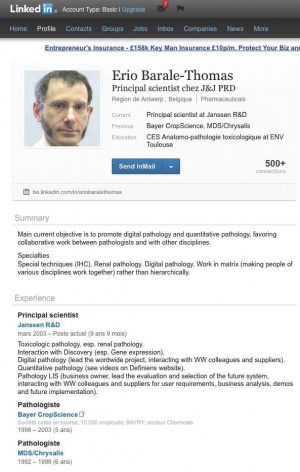
However, in his letter condemning Seralini, Barale-Thomas seems to have been less than open about his own conflicts of interest. He gives his affiliation in the letter only as president of the SFPT. But his LinkedIn page (29 November 2012) tells a different story. It states that since 2003 to the present he has been principal scientist at Janssen Biotech, a biotechnology company and subsidiary of the pharmaceutical company Johnson & Johnson.[4][5]
Confirming this position is a video "customer testimonial" by Barale-Thomas for digital technology, in which he is described as "Erio Barale-Thomas (Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical R&D, Beerse, Belgium)".[6]
Prior to joining Janssen he was a pathologist at the genetically modified crop and chemical company Bayer CropScience (1998-2003).[7]
Contents
Double standards?
In his critique of Séralini's study, Barale-Thomas argues that Séralini used too few animals (ten per sex per group, total of 20 per treatment group) and that his experiment was thus "underpowered"[8] - in other words, too weakly designed to justify conclusions drawn.
Yet in the GM industry's own experiments on GM foods conducted to gain regulatory approval, including Monsanto's 90-day study on the same NK603 maize that Séralini tested, only ten animals per sex per group, the same number that Séralini used, are analysed for blood and urine chemistry.[9][10] Furthermore, the GM company is free to choose which ten to analyse, allowing selection bias to enter the experiment and invalidating the results.
In an example of double standards, Barale-Thomas weighed in on the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) consultation on the design of these industry feeding studies on GM foods, complaining that the number of animals proposed for these experiments was too high. EFSA’s proposed 96 animals compares unfavorably in terms of experimental power with Séralini’s 200. But Barale-Thomas wanted EFSA to return to its previous suggestion of 80 or fewer.[11]
Barale-Thomas might reply that Seralini’s was a long-term experiment: he uses the word "long-term" in his complaint about Seralini's experiment being "underpowered" in his letter to the editor.[12] The implied argument is that in a long-term experiment, more rats are likely to die or get ‘spontaneous’ tumours as they age; so higher numbers of animals are required to ensure that the results are related to the treatment and not just the effects of old age. But then he claims that the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) guidelines recommend using groups of at least 50 animals per sex per group as saying they insist on 50 animals per sex per group "for the results to be considered valid".
But this argument is disingenuous. Barale-Thomas cites OECD guidelines for a carcinogenicity study - but Seralini’s was not a carcinogenicity study. It was a chronic toxicity study which happened to find tumours - which should be extended to a full-scale carcinogenicity study before the product can be claimed safe. Numbers of animals required to be used and analysed in in OECD protocols for chronic toxicity studies vary widely:
- OECD 408, the 90-day rodent feeding trials that Séralini decided to extend to a long-term period in his study, requires ten animals per sex per group.[13] This is the same number that Séralini used. It is also the same number that Monsanto analyzed for blood and urine chemistry in its 90-day tests on GMOs, including the test that concluded NK603 maize was safe to be marketed.[14]
- OECD 453, the combined chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity protocol, requires ten animals per sex per group for the chronic toxicity phase (the same number used by Séralini), but 50 per sex per group for the carcinogenicity phase.[15]
- OECD 452, the chronic toxicity protocol, requires 20 animals per sex per group, but only ten per sex per group must be analyzed for blood and clinical chemistry.[16]
- OECD carcinogenicity protocol 451 and the carcinogenicity phase of 453 require 50 animals per sex per group.[17][18]
And OECD itself stipulates that it requires 50 animals per sex per group "in order to increase the sensitivity of the study”, in other words, to ensure that a real toxic effect is not missed by an insensitive study with too few animals and to protect the public from a 'false negative' or false conclusion of safety.[19] Insensitivity of study design was not an issue with Seralini's study, as toxic effects were found. And unlike the industry studies submitted in support of marketing a product, which are supposed to conform to OECD protocols, Seralini's study was not performed to support marketing of a product, but to investigate toxicity. So it is irrelevant to apply OECD protocols to his study.
Contact
- Address:
- ...
- ...
- ...
- ...
- Phone:
- ...
- Email:
- ...
- Website:
- ...
Resources
Notes
- ↑ Barale-Thomas, E. (2012) Letter to the editor, Food and Chemical Toxicology. Available online 16 November 2012, acc 29 Nov 2012
- ↑ Barale-Thomas, E. (2012). Letter to the editor. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 16 Nov.
- ↑ Séralini, G. E., E. Clair, et al. (2012). Long term toxicity of a Roundup herbicide and a Roundup-tolerant genetically modified maize. Food and Chemical Toxicology 50(11): 4221-4231.
- ↑ LinkedIn, Erio Barale-Thomas, acc 29 Nov 2012, archived here
- ↑ Janssen Biotech Inc (2012)Home page, acc 29 Nov 2012
- ↑ Customer Testimonial: Erio Barale-Thomas, PhD, Johnson&Johnson, posted Oct 18 2012, acc 29 Nov 2012
- ↑ LinkedIn, Erio Barale-Thomas, acc 29 Nov 2012, archived here
- ↑ Barale-Thomas, E. (2012) Letter to the editor, Food and Chemical Toxicology. Available online 16 November 2012, acc 29 Nov 2012
- ↑ Hammond, B., R. Dudek, et al. (2004). "Results of a 13 week safety assurance study with rats fed grain from glyphosate tolerant corn." Food Chem Toxicol 42(6): 1003-1014.
- ↑ Hammond, B., J. Lemen, et al. (2006). "Results of a 90-day safety assurance study with rats fed grain from corn rootworm-protected corn." Food Chem Toxicol 44(2): 147-160.
- ↑ European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) (2011). "Outcome of the public consultation on the draft EFSA guidance on conducting repeated-dose 90-day oral toxicity study in rodents on whole food/feed." Supporting Publications 2011(205): 13.
- ↑ Barale-Thomas, E. (2012) Letter to the editor, Food and Chemical Toxicology. Available online 16 November 2012, acc 29 Nov 2012
- ↑ Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (1998). OECD guideline no. 408 for the testing of chemicals: Repeated dose 90-day oral toxicity study in rodents: Adopted 21 September 1998.
- ↑ Hammond, B., R. Dudek, et al. (2004). "Results of a 13 week safety assurance study with rats fed grain from glyphosate tolerant corn." Food Chem Toxicol 42(6): 1003-1014.
- ↑ Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2009). OECD guideline no. 453 for the testing of chemicals: Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity: Adopted 7 September 2009.
- ↑ Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2009). OECD guideline no. 452 for the testing of chemicals: Chronic toxicity studies: Adopted 7 September 2009.
- ↑ Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2009). "OECD guideline no. 451 for the testing of chemicals: Carcinogenicity studies: Adopted 7 September 2009."
- ↑ Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2009). OECD guideline no. 453 for the testing of chemicals: Combined chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity: Adopted 7 September 2009.
- ↑ Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) (2012). Guidance document 116 on the conduct and design of chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity studies, supporting test guidelines 451, 452 and 453: 2nd edition: Environment directorate joint meeting of the chemicals committee and the working party on chemicals, pesticides and biotechnology.